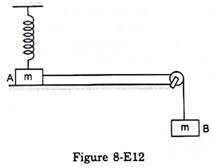
Figure (8-E12) shows two blocks A and B, each having a mass of 320 g connected by a light string passing over a smooth light pulley. The horizontal surface on which the block A can slide is smooth. The block A is attached to a spring of spring constant 40 N/m whose other end is fixed to a support 40 cm above the horizontal surface. Initially, the spring is vertical and unstretched when the system is released to move. Find the velocity of the block A at the instant it breaks off the surface below it. Take g = 10 m/s2.
The velocity of the block A is ![]()
Given
The masses of the blocks are given as 320 g, the spring constant is given as 40 N/m, the block B is attached at a height of 40cm from the horizontal surface, with a gravity of![]() .
.
Formula Used
The formula used to equate the conservation of the forces is given as Tension/Force equal to the product of spring constant/mass with compression distance/gravity.
![]()
![]()
![]()
where
T is the tension, k is the spring constant, m is the mass, x is the compression distance and g is the gravity.
Explanation
The formula used is the force or the tension, applied on the block A due to spring is given as
![]()
where X is taken as ![]() , so the tension due to spring is
, so the tension due to spring is
![]()
By equating the y-axis direction of the ![]() force is
force is
![]()
Placing the tension as![]() , we get the equation as
, we get the equation as
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now finding the value of the displacement x, we get the value as
![]()
![]()
Hence, the difference in Kinetic Energy is equivalent to the force applied on the block is written as
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore, the velocity of the block A is ![]()