Calculate the depression in the freezing point of water when 10 g of CH3CH2CHClCOOH is added to 250 g of water. Ka = 1.4 × 10–3, Kf = 1.86 K kg mol–1.
Given: Mass of CH3CH2CHClCOOH = 10 g
Mass of water = 250g
Ka = 1.4 × 10–3,
Kf = 1.86 K kg mol–1
Molar mass of CH3CH2CHClCOOH = 12 + 3 + 12 + 2 + 12 + 1 + 35.5 + 2 + 16 + 16 + 1
= 122.5 g mol–1
Number of moles of solute = ![]()
→ No. of moles = ![]()
∴ No. of moles = ![]() mol
mol
Now, Molality is given as,
![]()
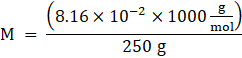
M = 0.3264 kg/mol
CH3CH2CHClCOOH ![]() CH3CH2CHClCOO- + H +
CH3CH2CHClCOO- + H +
Initial moles | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Equilibrium moles | (1-α) | α | α |
Total moles at equilibrium = (1-α) + 2 α
= 1 + α
In order to find out the depression in freezing point, ![]() f
f![]() f
f![]() values of i(vant Hoff’s factor) and α(degree of dissociation) are to be found out.
values of i(vant Hoff’s factor) and α(degree of dissociation) are to be found out.
To find out degree of dissociation, α
→ ![]()
Here, the value of α is negligible as compared to 1, and hence 1-![]() = 1, giving,
= 1, giving,
![]()
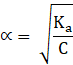
→![]()
∴ ![]()
To find out Vant Hoff’s factor,
→ ![]()
![]()
![]()
∴ ![]()
Now, to find out the depression in freezing point,
![]() f
f![]() f
f![]()
![]()
![]()
∴ ![]()
Thus, the depression in freezing point is ![]() f = 0.650C
f = 0.650C