AIM
To identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed (pea, gram or red kidney bean).
MATERIALS REQUIRED:
Seeds of Bengal gram /red kidney bean, forceps, cloth, magnifying glass, Petri dish, water.
THEORY
1. A seed is a ripened ovule with a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called sees coat, usually with some stored food.
2. The gram seed is formed within a small pod or legume.
3. It is light brown in colour.
4. Its surface may be smooth or wrinkled.
5. The furrow in the middle of seed bears a dark oval patch called chalaza.
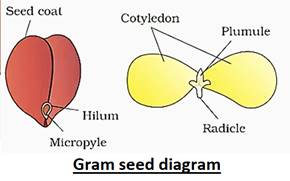
6. A seed has following parts, i.e., hilum, seed coat, an embryo, and endosperm.
7. The small oval scar present on the seed coat is called hilum.
8. In between the hilum and pointed end, a small pore called micropyle is present.
9. The seed soaks water through the micropyle during seed germination.
10. The labelled diagrams of pea seed, bean seed, and gram seed are shown below:


PROCEDURE
1. Take few dicot seeds like a pea or red kidney beans and leave them in water for overnight.
2. Next day, drain the excess water and cover the seeds with a moist cloth. Again keep the seeds aside for one day.
4. Then, peel off the seed coat carefully by using a pair of forceps.
5. Open the bean seed using a pair of forceps so that it falls into equal two halves.
6. Using a magnifying glass, try to locate the various parts of the beam embryo carefully.
7. Draw a labeled diagram of the inside of the dicot seed.

OBSERVATIONS
1. A seed coat encapsulates the various components of seed and provides physical protection from the environment.
2. Adjacent to hilum small pore is known as micropyle is present.
3. The embryo consists of two large, white and kidney-shaped cotyledons. The cotyledons are attached laterally to the curved embryonal axis.
4. The upper end of the embryonal axis is called plumule.
5. The part of embryo axis between radicle and attachment of cotyledon leaves is called hypocotyl. And, the part of embryo axis between plumule and attachment of cotyledon leaves is called epicotyl.
6. Rod-shaped and the slightly bulgy lower end of the embryonal axis which lies towards the micropylar end is called radicle.
RESULT
The embryo of dicot seeds consists of three main parts- plumule, radicle, and two cotyledons.
1. Plumule is the upper terminal part of the embryo which elongates and develop into the future shoot.
2. Radicle The lower end of embryo develops into the future root.
3. Cotyledons are also known as seed leaves and contain food for the baby plant.
PRECAUTIONS
1. The cloth which is used to cover seeds should be moist.
2. Seeds coat must be removed using a pair of forceps carefully so that the other part of the seed is not affected.
3. The seed after bisection must be handled with care.