Table of Contents
8
 INDIA : CLIMATE, VEGETATION AND WILDLIFE
INDIA : CLIMATE, VEGETATION AND WILDLIFE

You read in newspapers daily and watch on T.V. or hear others talking about weather. You must know that weather is about day to day changes in the atmosphere. It includes changes in temperature, rainfall and sunshine etc. For example, as such it may be hot or cold; sunny or cloudy; windy or calm. You must have noticed that when it is hot continuously for several days you don’t need any warm clothing. You also like to eat or drink cold things. In contrast there are days together, you feel cold without woollen clothes when it is very windy and chilly, you would like to have something hot to eat.
Broadly, the major seasons recognised in India are:
• Cold Weather Season (Winter) December to February
• Hot Weather Season (Summer) March to May
• Southwest Monsoon Season (Rainy)
June to September
• Season of Retreating Monsoon (Autumn) October and November
Cold Weather Season or Winter
During the winter season, the sun rays do not fall directly in the region. As a result the temperatures are quite low in northern India.
Hot Weather Season or Summer
In the hot weather season sun rays more or less directly fall in this region. Temperature becomes very high. Hot and dry winds called loo, blow during the day.

South West Monsoon Season or Rainy Season
This season is marked by the onset and advance of monsoon. The winds blow from Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal towards the land. They carry moisture with them. When these winds strike the mountain barriers, rainfall occurs.
Season of Retreating Monsoons or Autumn
Winds move back from the mainland to the Bay of Bengal. This is the season of the retreating monsoons. The southern parts of India, particularly Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh receive rainfall in this season.
However, the climate is about the average weather condition, which have been measured over many years.

The climate of India has broadly been described as Monsoon type. Monsoon is taken from the Arabic word ‘mausim’, which means seasons. Due to India’s location in the tropical region, most of the rain is brought by monsoon winds. Agriculture in India is dependent on rains. Good monsoons mean adequate rain and a bountiful crop.
The climate of a place is affected by its location, altitude, distance from the sea, and relief. Therefore, we experience regional differences in the climate of India. Jaisalmer and Bikaner in the desert of Rajasthan are very hot, while Drass and Kargil in Jammu and Kashmir are freezing cold. Coastal places like Mumbai and Kolkata experience moderate climate. They are neither too hot nor too cold. Being on the coast, these places are very humid. Mawsynram in Meghalaya receives the world’s highest rainfall, while in a particular year it might not rain at all in Jaisalmer in Rajasthan.
 Let’s Do
Let’s DoNatural Vegetation
We see a variety of plant life in our surroundings. How nice it is to play in a field with green grasses. There are also small plants called bushes and shrubs like cactus and flowering plants etc. Besides there are many tall trees some with many branches and leaves like neem, mango or some which stand with few leaves such as palm. The grasses, shrubs and trees, which grow on their own without interference or help from human beings are called natural vegetation. Do you wonder how these differ from each other. Different types of natural vegetation are dependent on different climatic conditions, among which the amount of rainfall is very important.
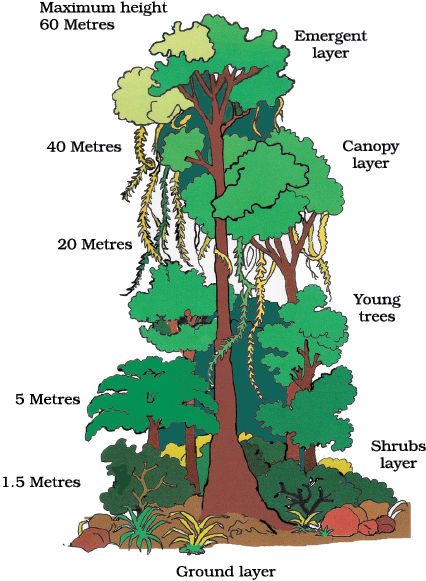

Figure 8.1 : Tropical Rain Forests
Due to varied climatic conditions, India has a wide range of natural vegetation.
Why are Forests Necessary?
Forests are very useful for us. They perform various functions. Plants release oxygen that we breathe and absorb carbon dioxide. The roots of the plants bind the soil; thus, they control soil erosion.
Forests provide us with timber for furniture, fuel wood, fodder, medicinal plants and herbs, lac, honey, gum, etc.
Forests are the natural habitat of wild life.
Natural vegetation has been destroyed to a large extent because of the reckless cutting of trees. We should plant more trees and protect the existing ones and make people aware of the importance of trees. We can have special programmes like Van Mahotsav to involve more people in making our earth green.
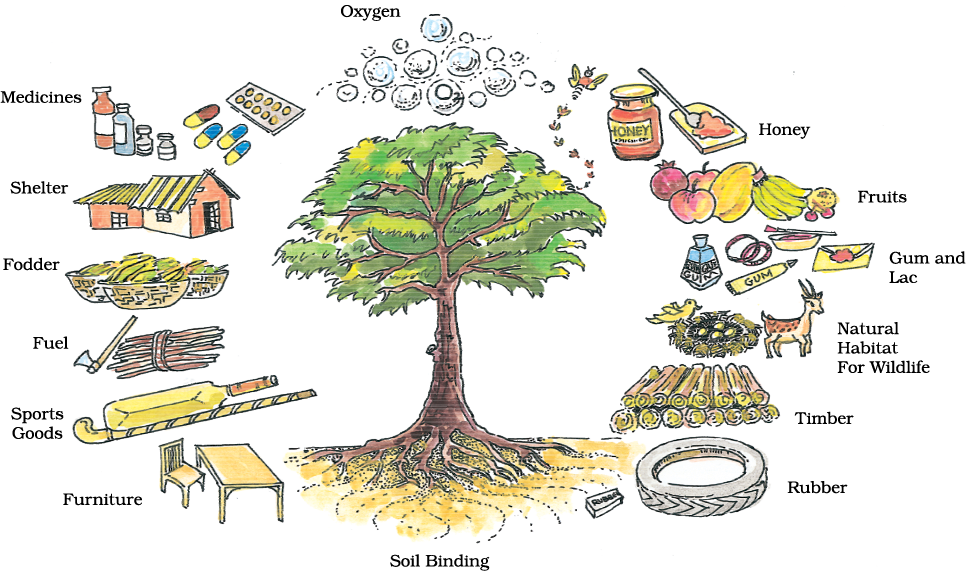


Figure 8.2 : What we get from forests
Wild Life
Forests are home to a variety of wild life. There are thousands of species of animals and a large variety of reptiles, amphibians, mammals, birds, insects and worms which dwell in the forest.
There are several hundreds of species of snakes found in India. Cobras and kraits are important among them.
Due to cutting of forests and hunting, several species of wildlife of India are declining rapidly. Many species have already become extinct.
In order to protect them many national parks, sanctuaries and biosphere reserves have been set up. The Government has also started Project Tiger and Project Elephant to protect these animals. Can you name some wildlife sanctuaries of India and locate them on a map?
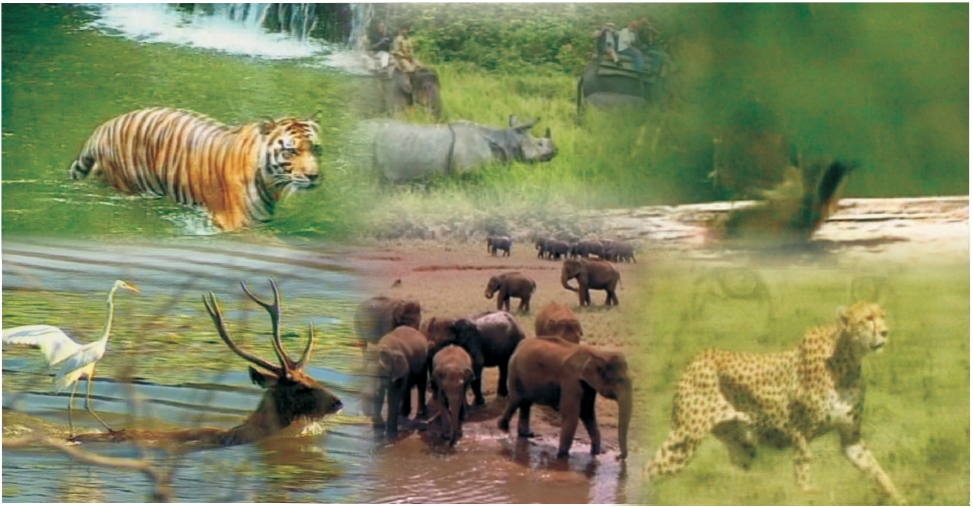

Figure 8.3 : Wildlife
You can also contribute in conserving wildlife. You can refuse to buy things made from parts of the bodies of animals such as their bones, horns, fur, skins, and feathers. Every year we observe wildlife week in the first week of October, to create awareness of conserving the habitats of the animal kingdom.

Figure 8.4
Why do poachers kill tigers?
What will happen if tigers vanish from our forests?
Have you ever visited any tiger reserves or a zoo where tigers are kept?
Migratory Birds
Some birds such as Pintail Duck, Curlews, Flamingo, Osprey and Little Stint migrate to our country in winter season every year. Smallest migratory bird Little Stint Weighing as low as 15 gram, from Arctic region travel over 8000 km to reach India.

1. Answer the following questions briefly.
(a) Which winds bring rainfall in India? Why is it so important?
(b) Name the different seasons in India.
(c) What is natural vegetation?
2. Tick the correct answers.
(a) The world’s highest rainfall occurs in
(i) Mumbai (ii) Asansol (iii) Mawsynram
(b) Wild goats and snow leopards are found in
(i) Himalayan region
(ii) Peninsular region
(iii) Gir forests
(c) During the south west monsoon period, the moisture laden winds
blow from
(i) land to sea (ii) sea to land (iii) plateau to plains
3. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Hot and dry winds known as ________________ blow during the day in the summers.
(b) The states of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu receive a great amount of rainfall during the season of________________.
(c) ________________ forest in Gujarat is the home of ________________.

1. Make a list of trees in your neighbourhood and collect pictures of plants, animals and birds and paste them in your copy.
2. Plant a sapling near your home and nurture it and write down the changes you observe for a few months.
3. Does any migratory bird come in your locality? Try to identify that. Be watchful in the winter season.
4. Visit a zoo in your city or visit a nearby forest or sanctuary with your elders. Look carefully at the various types of wildlife there.
Figure 8.4
Why do poachers kill tigers?
What will happen if tigers vanish from our forests?
Have you ever visited any tiger reserves or a zoo where tigers are kept?
APPENDIX II
Figure 8.4
Why do poachers kill tigers?
What will happen if tigers vanish from our forests?
Have you ever visited any tiger reserves or a zoo where tigers are kept?
APPENDIX II
Some Internet Sources for more information
http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/
www.nationalgeographic.com/earthpulse
http://www.cpcb.nic.in