Table of Contents

In Chapter 1 you have learnt that early human beings depended entirely on nature for food, clothing and shelter; but with time they learnt new skills to grow food, build homes and develop better means of transport and communication. In this way they modified the environment where they lived.
The place where a building or a settlement develops is called its site.
The natural conditions for selection of an ideal site are-
1. favourable climate
2. availability of water
3. suitable land
4. fertile soil
Settlements are places where people build their homes. Early human beings lived on trees and in caves. When they started to grow crops it became necessary to have a permanent home. The settlements grew near the river valleys as water was available and land was fertile. With the development of trade, commerce and manufacturing, human settlements became larger. Settlement flourished and civilizations developed near river valleys. Do you recall the names of civilization that grew along the banks of rivers Indus, Tigris, Nile and Hwang-He.
Settlements can be permanent or temporary. Settlements which are occupied for a short time
are called temporary settlements. The people living in deep forests, hot and cold deserts and mountains often dwell in such temporary settlements. They practice hunting, gathering, shifting cultivation and transhumance. However more and more settlements today are permanent settlements. In these settlements, people build homes to live in.

Fig. 7.1: Human Settlement
It was Mary’s birthday party. She and her friends were waiting for Gurpreet to arrive so that Mary could cut the cake. At last Gurpreet arrived- tired, coughing and wheezing. She explained that the traffic jam was terrible. Mary’s mother Mrs.Thomas patted Gurpreet’s back and sighed, “Oof! The pollution in our city!” Prasad had recently come from his village. He asked, “Why do we have such traffic jams and such pollution in the cities?” “The number of vehicles is increasing day by day due to the growing population in the cities”, Mary’s father, Mr. Thomas replied. Mary asked, “Then why are people coming to the cities?” Her mother replied, “They come looking for jobs, better education and medical facilities.” Mary further enquired, “If so many people keep coming to cities, where will all the people live?” Mr. Thomas said, “That is why you see so many slums and squatter settlements where people stay in congested and unhygienic conditions. Shortage of power and water supply are common problems in the cities”. Prasad said, “Our villages may not have big cinema halls, well-equipped schools and good hospitals, but we have lot of open spaces and fresh air to breathe in. When my grandfather was sick we had to rush him to the city hospital.”
Transhumance: It is a seasonal movement of people. People who rear animals move in search of new pastures according to changes in seasons.

From the above conversation we can identify two different pictures of settlements – the rural and the urban settlements. The villages are rural settlement where people are engaged in activities like agriculture, fishing, forestry, crafts work and trading etc. Rural settlements can be compact or scattered. A compact settlement is a closely built area of dwellings, wherever flat land is available
(Fig. 7.2). In a scattered settlement dwellings are spaced over an extensive area. This type of settlement is mostly found in hilly tracts, thick forests, and regions of extreme climate (Fig. 7.3).

Fig. 7.2: Compact Settlement

Fig. 7.3: Scattered Settlement
In rural areas, people build houses to suit their environment. In regions of heavy rainfall, they have slanting roofs. Places where water accumulates in the rainy season the houses are constructed on a raised platform or stilts (Fig. 7.4).
Thick mud walled houses with thatched roofs are very common in areas of hot climate. Local materials like stones, mud, clay, straw etc are used to construct houses.
The towns are small and the cities are larger urban settlements. In urban areas the people are engaged in manufacturing, trading, and services. Name some of the villages, towns and cities of your state.

Fig. 7.4: Houses on Stilts
Transport
Transport is the means by which people and goods move. In the early days it took a great deal of time, to travel long distances. People had to walk and used animals to carry their goods. Invention of the wheel made transport easier. With the passage of time different means of transport developed but even today people use animals for transport (Fig. 7.5).

Where do you find dwellings made of ice? Who makes them and what are they called?
Let's do
List the different modes of transport used by the students of your class while coming to school.

Fig. 7.5: Horse cart as a mode of transportation
Roadways
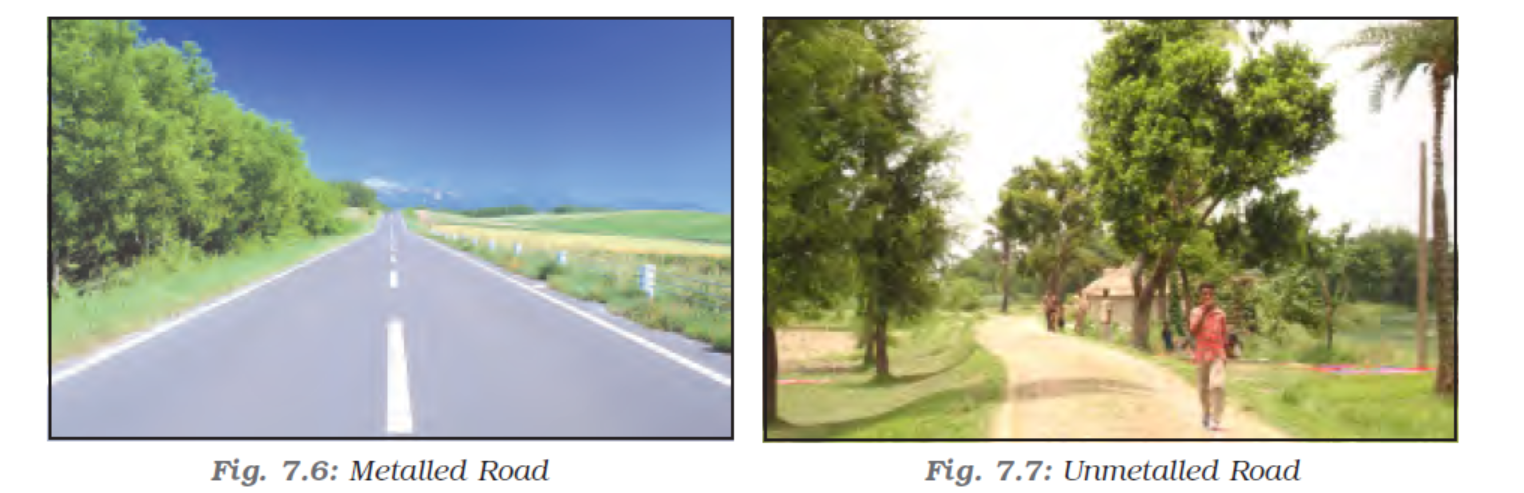

Railways
The railways carry heavy goods and people over long distances quickly and cheaply. The invention of the steam engine and the Industrial Revolution helped in speedy development of rail transport. Diesel and electric engines have largely replaced the steam engines. In places super fast trains have been introduced to make the journey faster. The railway network is well developed over the plain areas. Advanced technological skills have enabled laying of railway lines in difficult mountain terrains also. But these are much fewer in number. Indian railway network is well developed. It is the largest in Asia.
Do you know?
The train from Xining to Lhasa runs at an altitude of 4,000m above sea level and the highest point is 5,072 m

Do you know?
The Trans-Siberian Railway is the longest railway system connecting St. Petersburg in Western Russia to Vladivostok on the Pacific coast.
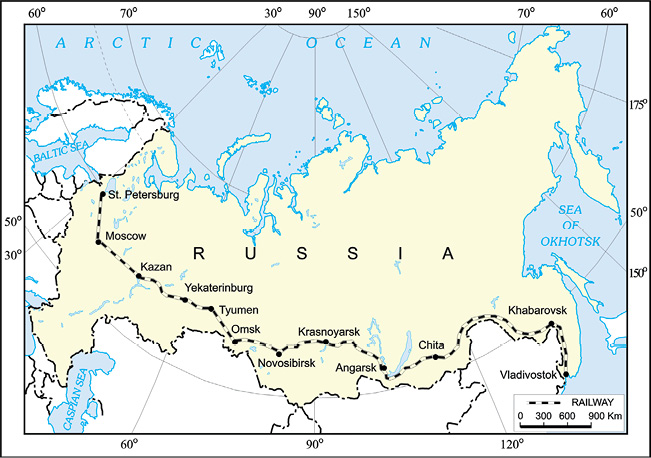
Trans – Siberian Railway
Waterways
You have already learnt that since early days waterways were used for transportation. Waterways are the cheapest for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances. They are mainly of two types – inland waterways and sea routes.
Navigable rivers and lakes are used as inland waterways. Some of the important inland waterways are the Ganga-Brahmaputra river system, the Great Lakes in North America and the river Nile in Africa
Sea routes and oceanic routes are mostly used for transporting merchandise and goods from one country to another. These routes are connected with the ports. Some of the important ports of the world are Singapore and Mumbai in Asia, New York, Los Angeles in North America, Rio de Janerio in South America, Durban and Cape Town in Africa, Sydney in Australia, London and Rotterdam in Europe (Fig. 7.11). Can you name some more ports of the world?

Fig. 7.8: Inland Waterways
Airways
This is the fastest way of transport developed in the early twentieth century. It is also the most expensive due to high cost of fuels. Air traffic is adversely affected by bad weather like fog and storms. It is the only mode of transport to reach the most remote and distant areas especially where there are no roads and railways. Helicopters are extremely useful in most inaccessible areas and in time of calamities for rescuing people and distributing food, water, clothes and medicines (Fig. 7.9). Some of the important airports are Delhi, Mumbai, New York, London, Paris, Frankfurt and Cairo (Fig. 7.11).

Fig. 7.9: A Helicopter
Communication
Communication is the process of conveying messages to others. With the development of technology humans have devised new and fast modes of communication. The Fig. 7.10 explains the evolution of the communication system.
Let's do
Find out the names of some newspapers and TV news channels in English, Hindi and a regional language.
The advancement in the field of communication has brought about an information revolution in the world. Different modes of communication are used to provide information, to educate as well as to entertain. Through newspapers, radio and television we can communicate with a large number of people. They are therefore called mass media. The satellites have made communication even faster. Satellites have helped in oil exploration, survey of forest, underground water, mineral wealth, weather forecast and disaster warning. Now we can send electronic mails or e-mails through Internet. Wireless telephonic communications through cellular phones have become very popular today. Internet not only provides us with worldwide information and interaction but has also made our lives more comfortable. Now we can reserve tickets for railways, airways and even cinemas and hotels sitting at home. With this kind of inter connectivity of people, services and institutions – across the world, we are a large global society.
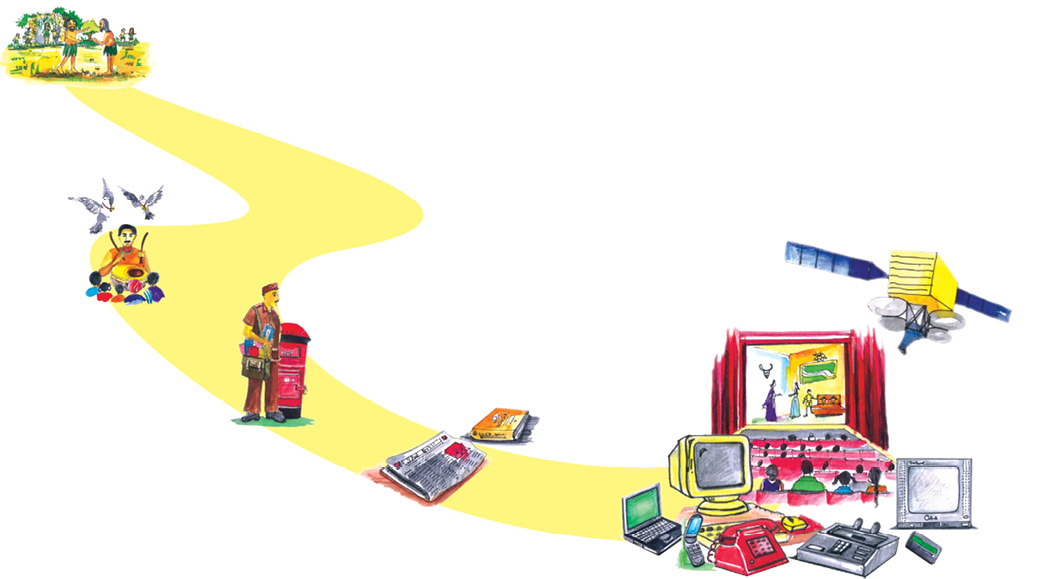

Fig. 7.10: Progress in the means of communication
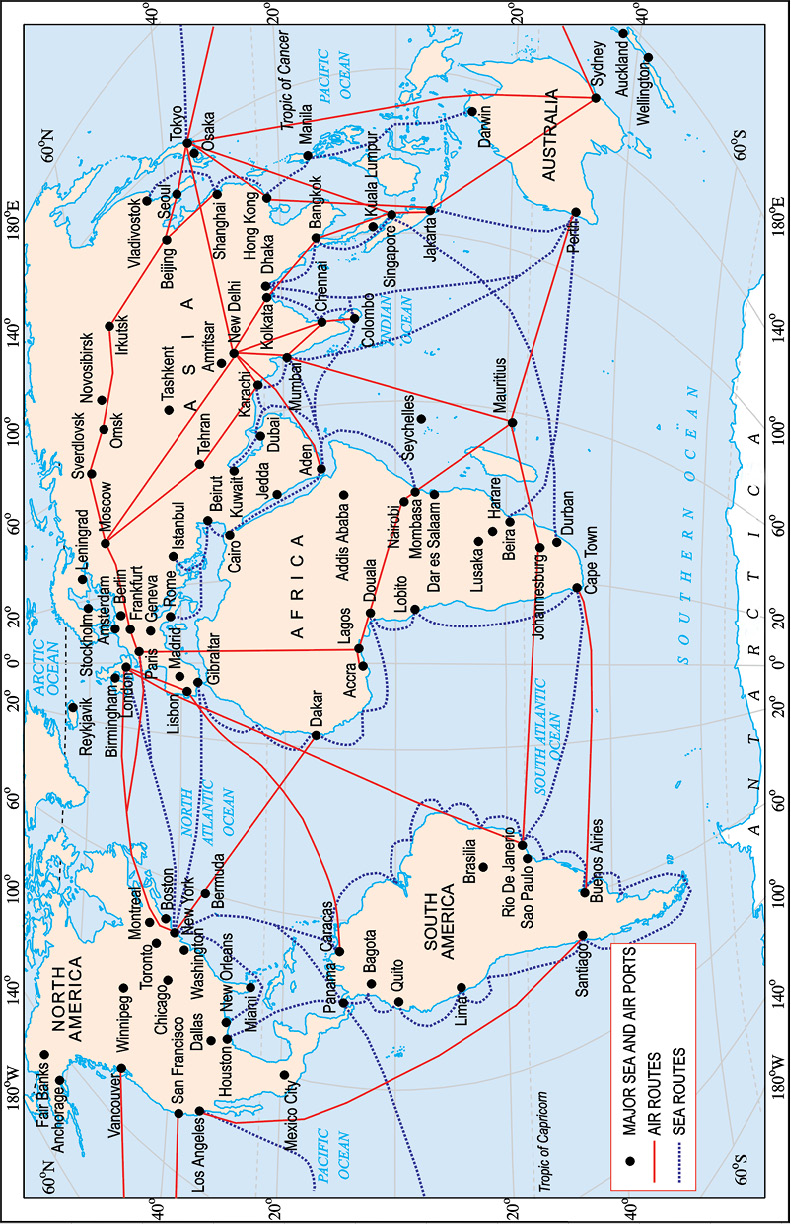
Fig. 7.11: World – Major Sea Ports and Airports

1. Answer the following questions.
(i) What are the four means of transport?
(ii) What do you understand by the term ‘settlement’?
(iii) Which are the activities practised by the rural people?
(iv) Mention any two merits of railways.
(v) What do you understand by communication?
(vi) What is mass media?
2. Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which is not a means of communication?
(a) telephone (b) books (c) table
(ii) Which type of road is constructed under the ground?
(a) fly over (b) expressways (c) subways
(iii) Which mode of transport is most suitable to reach an island?
(a) ship (b) train (c) car
(iv) Which vehicle does not pollute the environment
(c) cycle (b) bus (c) aeroplane
3. Match the following.
(i) Internet (a) areas where people are engaged in manufacturing, trade and services
(ii) Canal route (b) closely built area of houses
(iii) Urban areas (c) houses on stilts
(iv) Compact settlement (d) inland waterway
(e) a means of communication
4. Give reasons.
(i) Today’s world is shrinking.
5. For fun.
(i) Conduct a survey in your locality and find out how people commute to their respective workplaces using –
(a) more than two modes of transport
(b) more than three modes of transport
(c) stay within walking distance.
(ii) Mention which mode of communication you will prefer most in the following situations –
(a) Your grandfather has suddenly fallen ill. How will you inform the doctor?
(b) Your mother wants to sell the old house. How will she spread this news?
(c) You are going to attend the marriage of your cousin for which you will be absent from the school for the next two days. How will you inform the teacher?
(d) Your friend has moved out with his/her family to New York. How will you keep in touch on a daily basis?
