Table of Contents
Learning Objectives
After studying this chapter, you will be able to :
• state the meaning and need for the preparation of bank reconciliation statement;
• identify causes of difference between bank balance as per cash book and pass book;
• prepare the bank reconciliation statement;
• ascertain the correct bank balance as per cash book;
In chapter 4, you have learnt thatthe business organisations keep a record of their cash and bank transactions in a cash book. The cash book also serves the purpose of both the cash account and the bank account and shows the balance of both at the end of the period.
Once the cash book has been balanced, it is usual to check its details with the records of the firm’s bank transactions as recorded by the bank. To enable this check, the cashier needs to ensure that the cash book is completely up to date and a recent bank statement (or a bank passbook) has been obtained from the bank. A bank statement or a bank passbook is a copy of a bank account as shown by the bank records. This enable the bank customers to check their funds in the bank regularly and update their own records of transactions that have occurred. An illustrative bank passbook of a current account is shown in figure 5.1.
The amount of balance shown in the passbook or the bank statement must tally with the balance as shown in the cash book. But in practice, these are usually found to be different. Hence, we have to ascertain the causes for such difference. It will be observed that a bank statement/passbook shows all deposits in the credit column and withdrawals in the debit column. Thus, if deposits exceed withdrawals it shows a credit balance and if withdrawals exceed deposits it will show a debit balance (overdraft).
5.1 Need for Reconciliation
It is generally experienced that when a comparison is made between the bank balance as shown in the firm’s cash book, the two balances do not tally. Hence, we have to first ascertain the causes of difference thereof and then reflect them in a statement called Bank Reconciliation Statement to reconcile (tally) the two balances.
In order to prepare a bank reconciliation statement we need to have a bank balance as per the cash book and a bank statement as on a particular day along with details of both the books. If the two balances differ, the entries in both the books are compared and the items on account of which the difference has arisen are ascertained with the respective amounts involved so that the bank reconciliation statement may be prepared. Its format shown in figure 5.5.
Particulars Amount
₹
Balance as per cash book .......
Add: Cheques issued but not presented .......
Interest credited by the bank .......
Less: Cheques deposited but not credited by the bank .......
Bank charges not recorded in the cash book .......
Balance as per the passbook xxxx
Fig. 5.2 :Proforma of bank reconciliation statement
It can also be prepared with two amount columns one showing additions (+ column) and another showing deductions (-column). For convenience, we usually adopt this treatment.
Particulars Amount Amount
(+) (–)
Balance as per cash book ......
Cheques issued but not presented ` ......
Interest credited by the bank ......
Cheque deposited but not credited by the bank ......
Bank charges not recorded in the cash book ......
Balance as per the passbook. xxxx
Fig. 5.3 : Proforma of bank reconcitiation statement (table form)
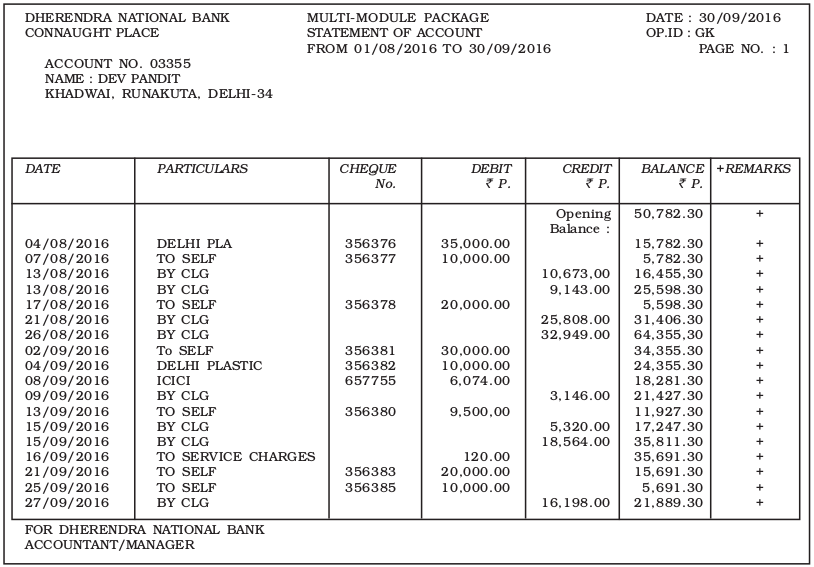
Fig. 5.1 :Specimen of bank statement (current account)
Reconciliation of the cash book and the bank passbook balances amounts to an explanation of differences between them. The differences between the cash book and the bank passbook is caused by:
• timing differences on recording of the transactions.
• errors made by the business or by the bank.
5.1.1 Timing Differences
When a business compares the balance of its cash book with the balance shown by the bank passbook, there is often a difference, which is caused by the time gap in recording the transactions relating either to payments or receipts. The factors affecting time gap includes :
5.1.1(a) Cheques issued by the bank but not yet presented for payment
When cheques are issued by the firm to suppliers or creditors of the firm, these are immediately entered on the credit side of the cash book. However, the receiving party may not present the cheque to the bank for payment immediately. The bank will debit the firm’s account only when these cheques are actually paid by the bank. Hence, there is a time lag between the issue of a cheque and its presentation to the bank which may cause the difference between the two balances.
5.1.1(b) Cheques paid into the bank but not yet collected
When firm receives cheques from its customers (debtors), they are immediately recorded in the debit side of the cash book. This increases the bank balance as per the cash book. However, the bank credits the customer account only when the amount of cheques are actually realised. The clearing of cheques generally takes few days especially in case of outstation cheques or when the cheques are paid-in at a bank branch other than the one at which the account of the firm is maintained. This leads to a cause of difference between the bank balance shown by the cash book and the balance shown by the bank passbook.
5.1.1(c) Direct debits made by the bank on behalf of the customer
Sometimes, the bank deducts amount for various services from the account without the firm’s knowledge. The firm comes to know about it only when the bank statement arrives. Examples of such deductions include: cheque collection charges, incidental charges, interest on overdraft, unpaid cheques deducted by the bank – i.e., stopped or bounced, etc. As a result, the balance as per passbook will be less than the balance as per cash book.
5.1.1(d) Amounts directly deposited in the bank account
There are instances when debtors (customers) directly deposits money into firm’s bank account. But, the firm does not receive the intimation from any source till it receives the bank statement. In this case, the bank records the receipts in the firm’s account at the bank but the same is not recorded in the firm’s cash book. As a result, the balance shown in the bank passbook will be more than the balance shown in the firm’s cash book.
5.1.1(e) Interest and dividends collected by the bank
When the bank collects interest and dividend on behalf of the customer, then these are immediately credited to the customers account. But the firm will know about these transactions and record the same in the cash book only when it receives a bank statement. Till then the balances as per the cash book and passbook will differ.
5.1.1(f) Direct payments made by the bank on behalf of the customers
Sometimes the customers give standing instructions to the bank to make some payment regularly on stated days to the third parties. For example, telephone bills, insurance premium, rent, taxes, etc. are directly paid by the bank on behalf of the customer and debited to the account. As a result, the balance as per the bank passbook would be less than the one shown in the cash book.
5.1.1(g) Cheques deposited/bills discounted dishonoured
If a cheque deposited by the firm is dishonoured or a bill of exchange drawn by the business firm is discounted with the bank is dishonoured on the date of maturity, the same is debited to customer’s account by the bank. As this information is not available to the firm immediately, there will be no entry in the firm’s cash book regarding the above items. This will be known to the firm when it receives a statement from the bank. As a result, the balance as per the passbook would be less than the cash book balance.
5.1.2 Differences Caused by Errors
Sometimes the difference between the two balances may be accounted for by an error on the part of the bank or an error in the cash book of the business. This causes difference between the bank balance shown by the cash book and the balance shown by the bank statement.
5.1.2(a) Errors committed in recording transaction by the firm
Omission or wrong recording of transactions relating to cheques issued, cheques deposited and wrong totalling, etc., committed by the firm while recording entries in the cash book cause difference between cash book and passbook balance.
5.1.2(b) Errors committed in recording transactions by the bank
Omission or wrong recording of transactions relating to cheques deposited and wrong totalling, etc., committed by the bank while posting entries in the passbook also cause differences between passbook and cash book balance.
Test Your Understanding - I
I. Read the following transactions and identify the cause of difference on the basis of time gap or errors made by business firm/bank. Put a sign (√ ) for the correct cause.
| S.No. | Transactions | Time Gap | Errors made by business/bank |
| 1. | Cheques issued to customers but not presented for payment. | ||
| 2. | Cheque amounting to ₹ 5,000 issued to M/s. XYZ but recorded as ₹ 500 in the cash book. | ||
| 3. | Interest credited by the bank but yet not recorded in the cash book. | ||
| 4. | Cheque deposited into the bank but not yet collected by the bank. | ||
| 5. | Bank charges debited to firm’s current account by the bank. |
II. Fill in the blanks :
(i) Passbook is a copy of.............as it appears in the ledger of the bank.
(ii) When money is with drawn from the bank, the bank ............. the account of the customer.
(iii) Normally, the cash book shows a debit balance, passbook shows .............balance.
(iv) Favourable balance as per the cash book means .............balance in the bank column of the cash book.
(v) If the cash book balance is taken as starting point the items which make the cash book balance smaller than the passbook must be .............for the purpose of reconciliation.
(vi) If the passbook shows a favourable balance and if it is taken as the starting point for the purpose of bank reconciliation statement then cheques issued but not presented for payment should be .............to find out cash balance.
(vii) When the cheques are not presented for payment, favourable balance as per the cash book is .............than that of the passbook.
(viii) When a banker collects the bills and credits the account passbook overdraft shows .............balance.
(ix) If the overdraft as per the passbook is taken as the starting point, the cheques issued but not presented are to be .............in the bank reconciliation statement.
(x) When the passbook balance is taken as the starting point items which makes the passbook balance .............than the balance in the cash book must be deducted for the purpose of reconciliation.
5.2 Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement
After identifying the causes of difference, the reconciliation may be done in the following two ways:
(a) Preparation of bank reconciliation statement without adjusting cash book balance.
(b) Preparation of bank reconciliation statement after adjusting cash book balance.
It may be noted that in practice, the bank reconciliation statement is prepared after adjusting the cash book balance, about which you will study later in the chapter.
5.2.1 Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement without adjusting Cash Book Balance
To prepare bank reconciliation statement, under this approach, the balance as per cash book or as per passbook is the starting item. The debit balance as per the cash book means the balance of deposits held at the bank. Such a balance will be a credit balance as per the passbook. Such a balance exists when the deposits made by the firm are more than its withdrawals. It indicates the favourable balance as per cash book or favourable balance as per the passbook. On the other hand, the credit balance as per the cash book indicates bank overdraft. In other words, the excess amount withdrawn over the amount deposited in the bank. It is also known as unfavourable balance as per cash book or unfavourable balance as per passbook.
We may have four different situations while preparing the bank reconciliation statement. These are :
1. When debit balance (favourable balance) as per cash book is given and the balance as per passbook is to be ascertained.
2. When credit balance (favourable balance) as per passbook is given and the balance as per cash book is to be ascertained.
3. When credit balance as per cash book (unfavourable balance/overdraft balance) is given and the balance as per passbook is to ascertained.
4. When debit balance as per passbook (unfavourable balance/overdraft balance) is given and the cash book balance as per is to ascertained.
5.2.1(a) Dealing with favourable balances
The following steps may be initiated to prepare the bank reconciliation statement:
(i) The date on which the statement is prepared is written at the top, as part of the heading.
(ii) The first item in the statement is generally the balance as shown by the cash book. Alternatively, the starting point can also be the balance as per passbook.
(iii) The cheques deposited but not yet collected are deducted.
(iv) All the cheques issued but not yet presented for payment, amounts directly deposited in the bank account are added.
(v) All the items of charges such as interest on overdraft, payment by bank on standing instructions and debited by the bank in the passbook but not entered in cash book, bills and cheques dishonoured etc. are deducted.
(vi) All the credits given by the bank such as interest on dividends collected, etc. and direct deposits in the bank are added.
(vii) Adjustment for errors are made according to the principles of rectification of erro₹ (The rectification of errors has been discussed in detail in chapter 6.)
(viii) Now the net balance shown by the statement should be same as shown by the passbook.
It may be noted that treatment of all items shall be the reverse of the above if we adjust passbook balance as the starting point. (see illustration 3)
The following solved illustrations will help you understand dealing with favourable balance as per cash book and passbook.
Illustration 1
From the following particulars of Mr. Vinod, prepare bank reconciliation statement as on March 31, 2017.
1. Bank balance as per cash book ₹ 50,000.
2. Cheques issued but not presented for payment ₹ 6,000.
3. The bank had directly collected dividend of ₹ 8,000 and credited to bank account but was not entered in the cash book.
4. Bank charges of ₹ 400 were not entered in the cash book.
5. A cheques for ₹ 6,000 was deposited but not collected by the bank.
Solution
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Mr. Vinod as on March 31, 2017
Particulars + –
₹ ₹
1. Balance as per cash book 50,000
2. Cheques issued but not presented for payment 6,000
3. Dividends collected by the bank 8,000
4. Cheque deposited but not credited by the bank 6,000
5. Bank charges debited by the bank 400
6. Balance as per passbook. 57,600
64,000 64,000
Illustration 2
From the following particulars of Anil & Co. prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on August 31, 2017.
1. Balance as per the cash book ₹ 54,000.
2. ₹ 100 bank incidental charges debited to Anil & Co. account, which is not recorded in cash book.
3. Cheques for ₹ 5,400 is deposited in the bank but not yet collected by the bank.
4. A cheque for ₹ 20,000 is issued by Anil & Co. not presented for payment.
Solution
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Anil & Co. as on August 31, 2017
Particulars + –
₹ ₹
1. Balance as per cash book 54,000 -
2. Cheqeus issued but not presented for payment 20,000 -
3. Cheques deposited but not credited by the bank - 5,400
4. Bank incidental charges debited by the bank - 100
5. Balance as per passbook - 68,500
74,000 74,000
Illustration 3
The bank passbook of M/s. Boss & Co. showed a balance of ₹ 45,000 on May 31, 2017.
1. Cheques issued before May 31, 2017, amounting to ₹ 25,940 had not been presented for encashment.
2. Two cheques of ₹ 3,900 and ₹ 2,350 were deposited into the bank on May 31 but the bank gave credit for the same in June, 2017.
3. There was also a debit in the passbook of ₹ 2,500 in respect of a cheque dishonoured on 31.5.2017. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on
May 31, 2017.
Solution
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Bose & Co as on May 31, 2017
Particulars + –
₹ ₹
1. Balance as per passbook 45,000
2. Cheques deposited but not collected by the bank 6,250
(₹ 3,900+ ₹ 2,350)
3. Cheque dishonoured recorded only in passbook 2,500
4. Cheques issued but not presented for payment 25,940
5. Balance as per cash book 27,810
53750 53750
5.2.1(b) Dealing with overdrafts
So far we have dealt with bank reconciliation statement where bank balances has been positive – i.e., there has been money in the bank account. However, businesses sometimes have overdrafts at the bank. Overdrafts are where the bank account becomes negative and the businesses in effect have borrowed from the bank. This is shown in the cash book as a credit balance. In the bank statement, where the balance is followed by Dr. (or sometimes OD) means that there is an overdraft and called debit balance as per passbook.
An overdraft is treated as negative figure on a bank reconciliation statement. The following solved illustration will help you understand the preparation of bank reconciliation statement when there is an overdraft.
Illustration 4
On March 31, 2017, Rakesh had on overdraft of ₹ 8,000 as shown by his cash book. Cheques amounting to ₹ 2,000 had been paid in by him but were not collected by the bank. He issued cheques of ₹ 800 which were not presented to the bank for payment. There was a debit in his passbook of ₹ 60 for interest and ₹ 100 for bank charges. Prepare bank reconciliation statement.
Solution
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Rakesh as on April 01, 2017
Particulars + –
₹ ₹
1. Overdraft as per cash book 8,000
2. Cheques deposited but not yet collectedcharged by the bank 2,000
3. Bank charges 60
4. Cheques issued but not presented for payment 800 100
5. Balance as per bank passbook (overdraft) 9,360
10,160 10,160
Illustration 5
On March 31, 2017 the bank column of the cash book of Agrawal Traders showed a credit balance of ₹ 1,18,100 (Overdraft). On examining of the cash book and the bank statement, it was found that :
1. Cheques received and recorded in the cash book but not sent to the bank of collection ₹ 12,400.
2. Payment received from a customer directly by the bank ₹ 27,300 but no entry was made in the cash book.
3. Cheques issued for ₹ 1,75,200 not presented for payment.
Interest of ₹ 8,800 charged by the bank was not entered in the cash book. Prepare bank reconciliation statement.
Solution
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Agarwal Traders as on March 31, 2017
Particulars + –
₹ ₹
1. Overdraft as per cash book 1,18,100
2. Cheques received and recorded in the cash book but not 12,400
sent to the bank for collection
3. Interest on bank overdraft debited by the bank but not 8,800
entered in the cash book
4. Payment received from the customer directly 27,300
5. Credited in the bank a/c but not entered in the cash book 1,75,200
6. Cheques issued but not presented for payment
7. Balance as per the passbook (favourable balance) 63,200
2,02,500 2,02,500
Illustration 6
From the following particulars of Asha & Co. prepare a bank reconciliation statement on December 31, 2017.
₹
Overdraft as per passbook 20,000
Interest on overdraft 2,000
Insurance Premium paid by the bank 200
Cheque issued but not presented for payment 6,500
Cheque deposited but not yet cleared 6,000
Wrongly debited by the bank 500
Solution
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Bose & Co as on May 31, 2017
Particulars + –
₹ ₹
1. Overdraft as per passbook 20,000
2. Interest on overdraft 2,000
3. Insurance premium paid by the bank 200
4. Cheque issued but not presented for payment 6,500
5. Cheques deposited but not yet cleared 6,000
6. Wrongly debited by the bank 500
7. Balance as per the cash book (overdraft) 17,800
26,500 26,500
Illustration 7
From the following particulars, prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on
March 31, 2017.
(a) Debit balance as per cash book is ₹ 10,000.
(b) A cheque for ₹ 1,000 deposited but not recorded in the cash book.
(c) A cash deposit of ₹ 200 was recorded in the cash book as if there is not bank, column therein.
(d) A cheque issued for ₹ 250 was recorded as ₹ 205 in the cash column.
(e) The debit balance of ₹ 1,500 as on the previous day was brought forward as a credit balance.
(f) The payment side of the cash book was under cast by ₹ 100.
(g) A cash discount allowed of ₹ 112 was recorded as ₹ 121 in the bank column.
(h) A cheque of ₹ 500 received from a debtor was recorded in the cash book but not deposited in the bank for collection.
(i) One outgoing cheque of ₹ 300 was recorded twice in the cash book.
Solution
Bank Reconciliation statement as on September 30, 2017
Particulars + –
₹ ₹
1. Debit balance as per cash book 10,000
2. Error in carrying forward 3,000
3. Cheque recorded twice in cash book 300
4. Cheque deposit not record in bank column 200
5. Cheque deposit but not recorded 1,000
6, Under casting of payment side 100
7. Cheque issued but not entered 250
8. A cash discount wrongly recorded in bank column 121
9. Cheque recorded but not deposited 500
10. Credit balance as per passbook 13,529
14,500 14,500
Illustration 8
From the following particulars, prepare the bank reconciliation statement of Shri Krishan as on March 31, 2017.
(a) Balance as per passbook is ₹ 10,000.
(b) Bank collected a cheque of ₹ 500 on behalf of Shri Krishan but wrongly credited it to Shri Kishan’s account.
(c) Bank recorded a cash book deposit of ₹ 1,589 as ₹ 1,598.
(d) Withdrawal column of the passbook under cast by ₹ 100.
(e) The credit balance of ₹ 1,500 as on the pass-book was recorded in the debit balance.
(f) The payment of a cheque of ₹ 350 was recorded twice in the passbook.
(g) The pass-book showed a credit balance for a cheque of ₹ 1,000 deposited by Shri Kishan.
Solution
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on March 31, 2017
Particulars + –
₹ ₹
1. Credit balance as per passbook 10,000
2. Cheque wrongly credited to another customer account 500
3. Error in carrying forward 3,000
4. Cheque recorded twice 350
5. Excess credit for cash deposit 9
6. Under casting of withdrawal column 100
7. Wrong credit 1,000
8. Debit balance as per cash book 12,741
13,850 13,850
Test Your Understanding - II
Select the Correct Answer:
1. A bank reconciliation statement is prepared by :
(a) Creditors (b) Bank
(c) Account holder in a bank (d) Debtors
2. A bank reconciliation statement is prepared with the balance :
(a) Passbook (b) Cash book
(c) Both passbook and cash book (d) None of these
3. Passbook is a copy of :
(a) Copy of customer Account (b) Bank column of cash book
(c) Cash column of cash book (d) Copy of receipts and payments
4. Unfavourable bank balance means :
(a) Credit balance in passbook (b) Credit balance in cash book
(c) Debit balance in cash book (d) None of these
5. Favourable bank balance means :
(a) Credit balance in the cash book(b) Credit balance in passbook
(c) Debit balance in the cash book (d) Both b and c
6. A bank reconciliation statement is mainly prepared for :
(a) Reconcile the cash balance of the cash book.
(b) Reconcile the difference between the bank balance shownby the cash book and bank passbook
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of these
Test your Understanding - III
State whether each of the following statements is True or False
1. Passbook is the statement of account of the customer maintained by the bank.
2. A business firm periodically prepares a bank reconciliation statement to reconcile the bank balance as per the cash book with the passbook as these two show different balances for various reasons.
3. Cheques issued but not presented for payment will reduce the balance as per the passbook.
4. Cheques deposited but not collected will result in increasing the balance of the cash book when compared to passbook.
5. Overdraft as per the passbook is less than the overdraft as per cash book when there are cheques deposited but not collected by the banker.
6. The debit balance of the bank account as per the cash book should be equal to the credit balance of the account of the business in the books of the bank.
7. Favourable bank balance as per the cash book will be less than the bank passbook balance when there are unpresented cheques for payment.
8. Direct collections received by the bank on behalf of the customers would increase the balance as per the bank passbook when compared to the balance as per the cash book.
9. When payments made by the bank as per the standing instructions of the customer, the balance in the passbook will be more when compared to the cash book.
Key Terms Introduced in the Chapter
1. Bank Reconciliation Statement
2. Cash book and Passbook
Summary with Reference to Learning Objectives
1. Bank Reconciliation Statement :A statement prepared to reconcile the bank balance as per cash book with the balance as per passbook or bank statement, by showing the items of difference between the two accounts.
2. Causes of difference :
– timing of recoding the transaction.
– error made by business or by the bank.
3. Correct cash balance:It may happens that some of the receipts or payments are missing from either of the books and errors, if any, need to be rectified. This arise the need to look at the entries/errors recorded in both statements and other information available and compute the correct cash balance before reconciling the statements.
Questions for Practice
Short Answers
1. State the need for the preparation of bank reconciliation statement?
2. What is a bank overdraft?
3. Briefly explain the statement ‘wrongly debited by the bank’ with the help of an example.
4. State the causes of difference occurred due to time lag.
5. Briefly explain the term ‘favourable balance as per cash book’
6. Enumerate the steps to ascertain the correct cash book balance.
Long Answers
1. What is a bank reconciliation statement. Why is it prepared?
2. Explain the reasons where the balance shown by the bank passbook does not agree with the balance as shown by the bank column of the cash book.
3. Explain the process of preparing bank reconciliation statement with amended cash balance.
Numerical Questions
Favourable balance of cash book and passbook –
1. From the following particulars, prepare a, bank reconciliation statement as at March 31, 2017.
(i) Balance as per cash book ₹ 3,200
(ii) Cheque issued but not presented for payment ₹ 1,800
(iii) Cheque deposited but not collected upto March 31, 2014 ₹ 2000
(iv) Bank charges debited by bank ₹ 150
(Ans: Balance as per passbook ₹ 2,850)
2. On March 31, 2017 the cash book showed a balance of ₹ 3,700 as cash at bank, but the bank passbook made up to same date showed that cheques for ₹ 700, ₹ 300 and ₹ 180 respectively had not presented for payment, Also, cheque amounting to ₹ 1,200 deposited into the account had not been credited. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement.
(Ans: Balance as per passbook ₹ 3,680).
3. The cash book shows a bank balance of ₹ 7,800. On comparing the cash book with passbook the following discrepancies were noted :
(a) Cheque deposited in bank but not credited ₹ 3,000
(b) Cheque issued but not yet present for payment ₹ 1,500
(c) Insurance premium paid by the bank ₹ 2,000
(d) Bank interest credit by the bank ₹ 400
(e) Bank charges ₹ 100
(d) Directly deposited by a customer ₹ 4,000
(Ans:Balance as per passbook ₹ 8,600).
4. Bank balance of ₹ 40,000 showed by the cash book of Atul on December 31, 2016. It was found that three cheques of ₹ 2,000, ₹ 5,000 and₹ 8,000 deposited during the month of December were not credited in the passbook till January 02, 2017. Two cheques of ₹ 7,000 and ₹ 8,000 issued on December 28, were not presented for payment till January 03, 2017. In addition to it bank had credited Atul for ₹ 325 as interest and had debited him with ₹ 50 as bank charges for which there were no corresponding entries in the cash book.
Prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on December 31, 2016.
(Ans:Balance as per passbook ₹ 40,275).
5. On comparing the cash book with passbook of Naman it is found that on March 31, 2014, bank balance of ₹ 40,960 showed by the cash book differs from the bank balance with regard to the following :
Bank charges Rs 100 on March 31, 2017, are not entered in the cash book.(a)
(b) On March 21, 2017, a debtor paid ₹ 2,000 into the company’s bank in settlement of his account, but no entry was made in the cash book of the company in respect of this.
(c) Cheques totaling ₹ 12,980 were issued by the company and duly recorded in the cash book before March 31, 2017, but had not been presented at the bank for payment until after that date.
(d) A bill for ₹ 6,900 discounted with the bank is entered in the cash book without recording the discount charge of ₹ 800.
st, 2017, but not credited by the bank until the following day.(e) ₹ 3,520 is entered in the cash book as paid into bank on March 31
(f) No entry has been made in the cash book to record the dishon or on March 15, 2017 of a cheque for ₹ 650 received from Bhanu.
Prepare a reconciliation statement as on March 31, 2017.
(Ans:Balance as per passbook ₹ 50,870).
6. Prepare bank reconciliation statement as on December 31, 2017. This day the passbook of Mr. Himanshu showed a balance of ₹ 7,000.
(a) Cheques of ₹ 1,000 directly deposited by a customer.
(b) The bank has credited Mr. Himanshu for ₹ 700 as interest.
(c) Cheques for ₹ 3000 were issued during the month of December but of these cheques for ₹ 1,000 were not presented during the month of December.
(Ans:Balance as per cash book ₹ 3,300).
7. From the following particulars prepare a bank reconciliation statement showing the balance as per cash book on December 31, 2016.
(a) Two cheques of ₹ 2,000 and ₹ 5,000 were paid into bank in October, 2016 but were not credited by the bank in the month of December.
(b) A cheque of ₹ 800 which was received from a customer was entered in the bank column of the cash book in December 2016 but was omitted to be banked in December, 2016.
(c) Cheques for ₹ 10,000 were issued into bank in November 2016 but not credited by the bank on December 31, 2016.
(d) Interest on investment ₹ 1,000 collected by bank appeared in the passbook.
Balance as per Passbook was ₹ 50,000
(Ans:Balance as per cash book ₹ 47,800)
8. Balance as per passbook of Mr. Kumar is 3,000.
(a) Cheque paid into bank but not yet cleared
Ram Kumar ₹ 1,000
Kishore Kumar ₹ 500
(b) Bank Charges ₹ 300
(c) Cheque issued but not presented
Hameed ₹ 2,000
Kapoor ₹ 500
(d)Interest entered in the passbook but not entered in the cash book ₹ 100
Prepare a bank reconciliation statement.
(Ans:Balance as per cash book ₹ 2,200).
9. The passbook of Mr. Mohit current account showed a credit Balance of₹ 20,000 on dated December 31, 2016. Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement with the following information.
(i) A cheque of ₹ 400 drawn on his saving account has been shown on current account.
stcheque was presented for payment.(ii) He issued two cheques of ₹ 300 and ₹ 500 on of December 25, but only the I
(iii) One cheque issued by Mr. Mohit of ₹ 500 on December 25, but it was not presented for payment whereas it was recorded twice in the cash book.
(Ans:Balance as per cash book ₹ 18,900).
Unfavourable balance of cash book
10. On Ist January 2017, Rakesh had an overdraft of ₹ 8,000 as showed by his cash book. Cheques amounting to ₹ 2,000 had been paid in by him but were not collected by the bank by January 01, 2017. He issued cheques of ₹ 800 which were not presented to the bank for payment up to that day. There was a debit in his passbook of ₹ 60 for interest and ₹ 100 for bank charges. Prepare bank reconciliation statement for comparing both the balance.
(Ans :Overdraft as per passbook ₹ 9,360)
11. Prepare bank reconciliation statement.
(i) Overdraft shown as per cash book on December 31, 2017 ₹ 10,000.
(ii) Bank charges for the above period also debited in the passbook₹ 100.
7₹ 380 debited in the passbook.(iii) Interest on overdraft for six months ending December 31, 201
(iv) Cheques issued but not incashed prior to December 31, 2017 amounted to ₹ 2,150.
(v) Interest on Investment collected by the bank and credited in the passbook ₹ 600.
(vi) Cheques paid into bank but not cleared before December, 31, 2017 were ₹ 1,100.
(Ans:overdraft as per passbook ₹ 8,830).
12. Kumar find that the bank balance shown byhis cash book on December 31, 2017 is ₹ 90,600 (Credit) but the passbook shows a difference due to the following reason:
A cheque (post dated) for ₹ 1,000 has been debited in the bank column of the cash book but not presented for payment. Also, a cheque for₹ 8,000 drawn in favour of Manohar has not yet been presented for payment. Cheques totaling ₹ 1,500 deposited in thebank have not yet been collected and cheque for ₹ 5,000 has been dishonoured.
(Ans:overdraft as per passbook ₹ 90,100).
13. On December 31, 2017, the cash book of Mittal Bros. Showed an overdraft of ₹ 6,920. From the following particulars preparea Bank Reconciliation Statement and ascertain the balance as per passbook.
(1) Debited by bank for ₹ 200 on account of Interest on overdraft and ₹ 50 on account of charges for collecting bills.
encashed before December, 31, 2017 for₹ 4,000.(2) Cheques drawn but not
(3) The bank has collected interest and has credited ₹ 600 in passbook.
(4) A bill receivable for ₹ 700 previously discounted with the bank had been dishonoured and debited in the passbook.
(5) Cheques paid into bank but not collected and credited before December 31, 2017 amounted ₹ 6,000.
(Ans :Overdraft as per passbook ₹ 9,170).
Unfavourable balance of the passbook
14. Prepare bank reconciliation statement of Shri Bhandari as onMarch31, 2017
(i) The Payment ofacheque for ₹ 550 was recorded twice in the passbook.
(ii) Withdrawal column of the passbook under cast by ₹ 200
(iii) A Cheque of ₹ 200 has been debited in the bank column of the Cash Book but it was not sent to bank at all.
(iv) A Cheque of ₹ 300 debited to Bankcolumn of the cash book was not sent to the bank.
(v) ₹ 500 in respect of dishonoured cheque were entered in the passbook but not in the cash book.
Overdraft as per passbook is ₹ 20,000.
(Ans:Overdraft as per cash book ₹ 21,350).
15. Overdraft shown by the passbook of Mr. Murli is ₹ 20,000. Prepare bank reconciliation statement on dated March 31, 2017.
(i) Bank charges debited as per passbook ₹ 500
(ii) Cheques recorded in the cash book but not sent to the bank for collection ₹ 2,500
(iii) Received a payment directly from customer ₹ 4,600.
(iv) Cheque issued but not presented for payment ₹ 6,980.
(v) Interest credited by the bank ₹ 100.
(vi) LIC paid by bank ₹ 2,500.
(vii) Cheques deposited with the bank but not collected ₹ 3,500.
(Ans: Overdraft as per cash book ₹ 22,680).
16. Raghav & Co. have two bank accounts. Account No. I and Account No. II. From the following particulars relating to Account No. I, find out the balance on that account of March 31, 2017 according to the cash book ofthe firm.
(i) Cheques paid into bank prior toMarch 31, 2017, but not credited for ₹ 10,000.
(ii) Transfer of funds from account No. II to account no. I recorded by the bank on March 31, 2017 but entered in the cash book after that date for ₹ 8,000.
(iii) Cheques issued prior to March 31, 2017 but not presented until after that date for ₹ 7,429.
(iv) Bank charges debited by bank not entered in the cash book for₹ 200.
(v) Interest Debited by the bank not entered in the cash book ₹ 580.
(vi) Overdraft as per Passbook ₹ 18,990.
(Ans:Overdraft as per cash book ₹ 23,639).
17. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement from the following particularsand show the balance as per cash book.
(i) Balance as per passbook onMarch 31, 2017 overdrawn₹ 20,000.
(ii) Interest on bank overdraft not entered in the cash book ₹ 2,000.
(iii) ₹ 200 insurance premium paid by bank has not been entered in the cash book.
(iv) Cheques drawn in the last week ofMarch 2017, but not cleared till date for ₹ 3,000 and ₹ 3,500.
(v) Cheques deposited into bank on February 2017, but yet to be credited on dated March 31, 2017 ₹ 6,000.
(vii) Wrongly debited by bank ₹ 500.
(Ans:Overdraft as per cash book ₹ 17,800).
18. The passbook of Mr. Randhir showed an overdraft of ₹ 40,950 on March 31,2017.
Prepare bank reconciliation statement on March 31, 2017.
(i) Out of cheques amounting to ₹ 8,000 drawn by Mr. Randhir on March 27 a cheque for ₹ 3,000 was encashed on April2017.
(ii) Credited by bank with ₹ 3,800 for interest collected by them, but the amount is not entered in the cash book.
(iii) ₹ 10,900 paid in by Mr. Randhir in cash and by cheques on March, 31 cheques amounting to ₹ 3,800 were collected on April, 07.
(iv) A Cheque of ₹ 780 credited in the passbook on March 28 being dishonoured is debited again in the passbook on April 01, 2017. There was no entry in the cash book about the dishonour of the cheque until April 15.
(Ans:Overdraft as per cash book ₹ 43,170)
Checklist to Test Your Understanding
Test Your Understanding - I
(I) 1. Time gap 2. Error 3. Time gap
4. Time gap 5. Time gap
(II) (i) Customer account (ii) Debit (iii) Credit
(iv) Debit (v) Added (vi) Deducted
(vii) loss (viii) Loss (ix) Added
(x) Higher
Test Your Understanding - II
1. (b) 2. (c) 3. (a) 4. (a) 5. (c) 6. (b)
Test Your Understanding - III
1. (T) 2. (T) 3. (F) 4. (T) 5. (F) 6. (T) 7. (T) 8. (T) 9. (F)
