Table of Contents
5
Electronic Presentation Tool
Objectives
After completing this Chapter, the student will be able to:
- design different types of slides,
- recognise type of views of presentation,
- insert graphics, audio and video in a presentation,
- copy and move text and slides within and between presentation files,
- apply designs in slides, adding animation effects to the text,
- add slide transition effects, and hyper linking,
- create action buttons,
- run a slide show and
- pack a presentation file to run it on a computer not having the presentation software.
“Projected slides should be as visual as possible and support your points quickly, efficiently and powerfully.”
Garr Reynolds
(Associate Professor of Management at Kansai Gaidai University)
Introduction
For our school exhibition, we want to prepare an exhibit on any current issue – global warming, drug abuse or child labour. We could prepare our exhibit in the conventional way, i.e. by using static tools, like charts and posters and maybe some visual images. Imagine the impact if, instead of the charts, we have music, moving objects and graphics displaying the message.
The objective of the exhibition is to make our message understood and remembered by others. An average human being has a very short attention span. Audio-visual aids can make presentations more interesting, dynamic and effective. Therefore, we can make it more interesting and attention seeking by making the characters move/dance, use pictures/charts/graphics, play music or show video. Thus we manage to create a much better impression. How can we do this?
5.1 An Electronic Presentation
An electronic presentation program is used to display information. This information is normally displayed in the form of a slide show – the information is shown on a slide which is viewed on a computer’s monitor, or beamed on a screen using a LCD projector. A presentation can have several slides, which can be displayed one after the other. The information presented can be an assortment of text, graphics, audio and video.
Why do we call the screen of information a slide? The word slide is a reference to the slide projector, which is somewhat obsolete today, thanks to electronic presentation software. In the days of slide projectors, each slide had to be shot by a camera, specially developed in a studio, and then placed on a slide projector for projection on a screen. Today, however, we can just design our slide on a computer using a presentation software and project it.
There are different types of presentations like professional (work-related), educational and for general communication. Presentation programs can either supplement or replace the use of older visual aid technology, such as pamphlets, handouts, chalkboards, flip charts, posters, slides and overhead transparencies.
A commonly used presentation program is Microsoft PowerPoint, although there are alternatives such as OpenOffice.org, Impress, Corel Presentations and Apple’s Keynote. A presentation program includes three major components: an editor that allows text to be inserted and formatted; a method for inserting graphic images, audio and video; and a slide-show system to display the final content.
In this chapter, we are using the presentation package – Microsoft PowerPoint – as our learning tool. However, we should remember that other such programs are also available. If we learn to use one of them, we will be able to use the others without any difficulty.
5.2 Starting the Presentation program
Whatever the presentation program we are using, we can start it from the Program option under the Windows Start menu. For example, to start Microsoft PowerPoint, click on
 , then on
, then on![2772.png]() , and lastly on
, and lastly on![2777.png]()
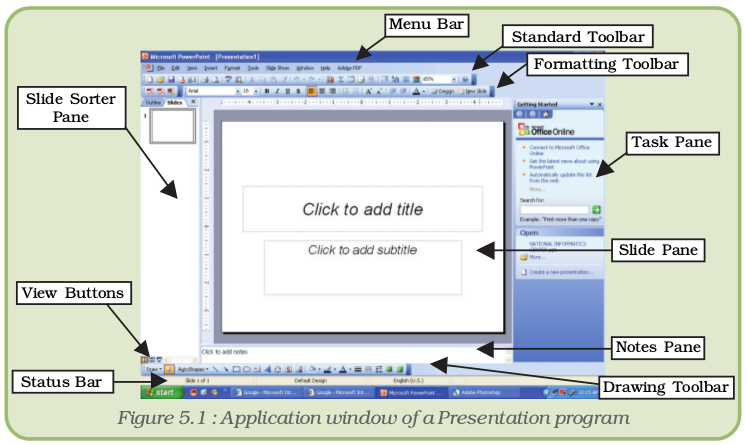
5.2.1 Anatomy of the Application Window
Any presentation software that we use will allow us to design and show slides. The application window (i.e., Microsoft PowerPoint window, Openoffice.org Impress window, etc.) will provide us with tools that will assist us in our job (Figure 5.1). The important components of this window are:
- Menu Bar : Provides menu options to help in designing and viewing the presentation.
- Standard Toolbar : Contains tools for standard tasks, like saving, printing, cutting, copying, pasting, etc.
- Formatting Toolbar : Provides tools for formatting like bold, italic, underline, etc.
- Task Pane : Allows options depending on the selected task. The figure 5.1 shows the options for the task New Presentation. We can select other tasks too.
- Slide Pane : This is the place where we design the slide by typing, formatting, etc.
- Slide Sorter Pane : Allows us to decide on the order in which the slides will be shown during the slide show.
- Notes Pane : Allows us to type in notes that we may need while preparing for the presentation later, but will not be shown during the slide show.
- View Buttons : Provides options to decide whether we want to view slide show, normal slide view, or slide sorter view.
- Drawing ToolBar : Provides tools for drawing basic shapes, inserting pictures, changing colours, etc.
- Status Bar : This provides information about the current presentation, like the number of slides, the design applied, etc.
After learning documentation and spreadsheet packages, we are already quite familiar with menu bar, standard toolbar, formatting toolbar, drawing toolbar, and the status bar.
5.3 Starting A New Presentation
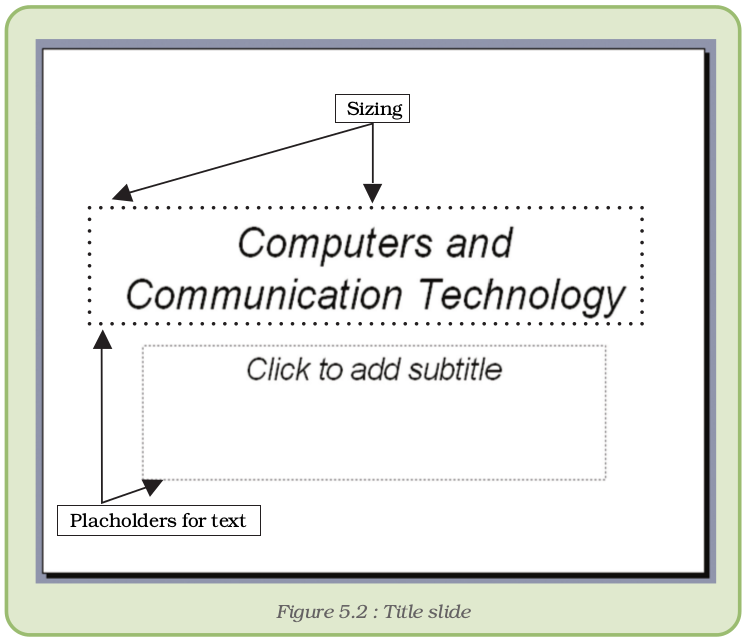
To create a new presentation, click on Blank Presentation on the New Presentation task pane. We will now see a slide on the slide pane similar to the one shown in Figure 5.1. This is called the title slide.
The first step to start with any presentation software is to type in some text in the slides.
It is not necessary that we have to type in something in every placeholder in the slide. For example, if we do not have any subtitle, just leave the corresponding placeholder as it is. The text ‘Click to add subtitle’ will not be seen on the screen when we run the slide show.
Let us now prepare our first presentation:
- Open the Presentation Program, click on the placeholder (Figure 5.2 ) which says – Click to add title, and type text.
- Click to add subtitle, and type the name.
5.3.1 ADDING A NEW SLIDE
Click on New Slide option on Insert menu or (CTRL + M) and select a desired layout from the Slide Layout options in the Task Pane. (Appendix 5.1–5.3)
5.3.2 Views in Presentation
A presentation can be viewed in several ways as per the location and demand. Some presentation options are listed below:
Normal View : This view has three panes and shows the outline, the notes area and the slide. We can type the notes in this place holder which we might require at the time of showing our presentation. Text in the notes page does not appear in the slide show.
Outline View : In this view we can see only the text of the slides in the presentation.
Slide Sorter View : In this view, slides appear of thumbnail size and they can be moved or sorted according to the requirement. Slides can be moved by first clicking them and dragging them to their desired location.
Slide Show : This view is used to show the final presentation with all the effects and colour schemes.
5.3.3 Insert Other Objects
The following is a list of various objects that can be inserted on a slide.
Table : Allows us to insert a table. We can insert the number of rows and columns required for the table, and then type in the content.
Chart : Allows us to insert a chart. We can type in the data values in order to develop the chart.
Clip Art : Allows us to insert a clip art, a variety of which normally comes along with the presentation software.
Picture : Allows us to insert picture – the ones that we might have clicked using a digital camera, or have scanned using a scanner, or have got from somewhere else. We have to provide the name of the picture file we wish to insert.
Diagram or Organisational Chart : Allows us to insert diagrams which we can select from the diagram gallery. One of the common options is the organisational chart (a chart showing hierarchy in an organisation, or a family tree, etc.).
Media Clip : Allows us to insert a media clip like some audio or video clips. However, to insert a media clip in this manner, Microsoft PowerPoint requires that the media clip be a part of Microsoft Clip Organiser.
Figure 5.3 shows a slide layout which can be used to insert non-text content:

Place the mouse over the desired non-text content and click to include the same on the slide.
We have already read about inserting Clip Art in the presentation by selecting a slide layout that allows us to insert non-text content. There is another way of inserting clip art into the slide. Let us learn this process:
- Open the presentation.
- Click on Clip Art under Picture option of Insert menu. We will now see the Insert Clip Art option in the task pane.
- We can insert some text to search clip arts belonging to a particular group. To try out, let us type in Inspiration and click on
![2782.png]() . If we are not sure, just click on
. If we are not sure, just click on ![2787.png]() without typing in any text.
without typing in any text. - We will see all the available clip arts grouped under our search text in the task pane.
- Select the desired clip art by clicking on it.
- We will now get the clip art on the slide. We can change its size by dragging the sizing handles. By click and drag we can place the clip art at the desired location in the slide.
5.3.4 Create a Chart in Presentation
Sometimes it is useful to project a chart to the audience rather than listing out raw data. We have learnt how to design charts using spreadsheets. Now we will learn how we can get a chart in presentation software:
- Open the slide where we want to place the chart.
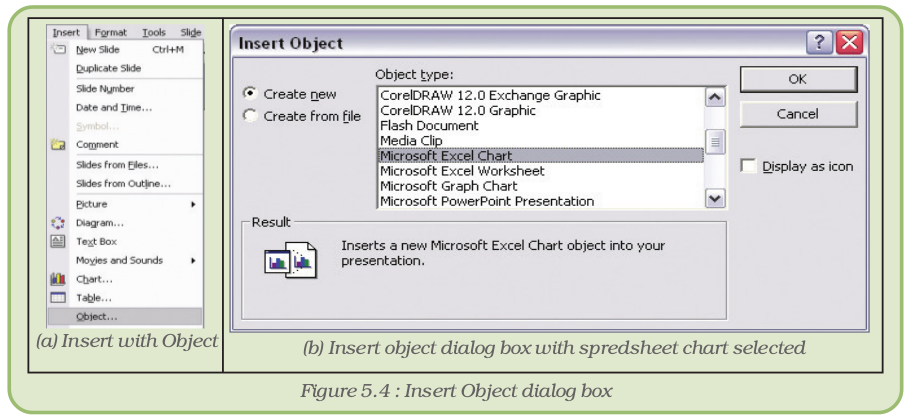
- Generally a Presentation software cannot draw charts. We need to get the help of some other software. Click on Object under Insert menu (Figure 5.4 (a)).
If we plan to draw the chart in spreadsheet, select Microsoft Excel Chart (Figure 5.4 (b)) under Object type and click on OK.
A dummy chart (Figure 5.5) appears on our slide which can be modified with our data.

- At the bottom of the chart we will notice
![2792.png]() . Click on Sheet1 and feed in the data for the chart as we had done in the spreadsheet.
. Click on Sheet1 and feed in the data for the chart as we had done in the spreadsheet. - We can change what the chart looks like by using the options under the Chart menu. (As in spreadsheet)
5.3.5 Navigating Across Slides
Now that we have more than one slide in our presentation, we will need to move from one to the other while designing them. We have three different options for this:
- Press the Page Up (or PgUp) key to go to the previous slide, press Page Down (or PgDn) key to move to the next slide.
- Click on the appropriate slide on the Slide Sorter pane.
- Use the scroll bar that appears between the Slide Pane and the Task Pane.
5.4 Saving and Opening a Presentation
Once made, we would surely like to save the presentation (i.e., store it permanently) for future reference and use. The process of saving a presentation and later opening it (or to create a new presentation) is similar to what we have learnt in Chapter 3 (Word Processing Tool).
Note : If we add or edit anything after we have saved the presentation, we will have to save it once again. Otherwise, the changes made after the last Save operation will not be saved.
We had previously typed in some text in the a slides of the presentation. Now we save it with a filename, My Presentation.
5.5 Formatting Text
Now let us learn how to make the slide more presentable by formatting the text on the slides:
We can format the text either through the Format option under the Menu Bar, or we can use the Formatting Toolbar to invoke most (but not all) formatting options (as in word processing). The main formatting options are –
- Font
- Bullets and Numbering
- Alignment.
Before we format any text, we must select the part of the text we want to format. For Font formatting, we need to select all the characters that we want to format; while for the others, we need to select any part of the paragraph.
5.6 Copy, move and delete text and slides
For copying, moving or deleting text from and to the same or different slide in the same or different presentation we can follow the same procedure as in the case of word processing. When we copy a slide, we actually duplicate the slide. When we move a slide, we end up changing the order of the slide in the presentation. These can be done as follows:
- To copy, i.e. duplicate a slide, select the slide (on the Slide Pane or in the Slide Sorter Pane) and click on Insert
![2797.png]() Duplicate Slide.
Duplicate Slide. - To move a slide or a group of slides, select the slide(s) in the Slide Sorter Pane and drag them to the desired location.
- To delete a slide or a group of slides, select the slide(s) in the Slide Sorter Pane and press the Delete key.
Note : To select multiple contiguous slides, press the Shift key as you click on the slides one after the other. You can also select the first one, and then click on the last one while keeping the Shift key pressed. To select non-contiguous slides, press the Ctrl key instead of the Shift key.
5.7 How to view slides?
Most presentation software will provide us with three views:
- Normal view – where we design the presentation.
- Slide Sorter view – this is a view of the slides in the presentation in thumbnail form. When we have finished creating and editing the presentation, slide sorter view gives us an overall picture of it – making it easy to reorder, add, or delete slides.
- Slide Show view – this takes up the full computer screen. This is the view that we will use at the time of presentation.
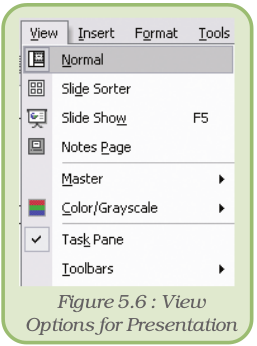
We can move from one view to another by using the options under the View menu or by clicking on the appropriate View Buttons.
The options under the View menu are given in figure 5.6.
5.8 Slide Show : Present slides to the audience
Now that we have somewhat prepared the presentation, its time to view the show. We are already familiar with the Slide Show option under View menu and the corresponding View button. We can use either of them to start the slide show. We can also start the slide show by selecting the View Show option under the Slide Show menu.
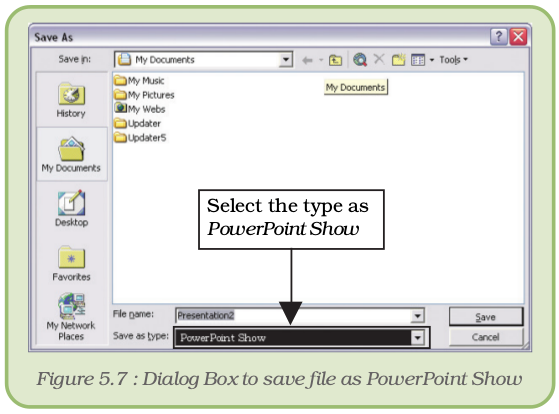
We can also save the presentation file as PowerPoint Show. In that case, we will not have to start the presentation program to view the presentation. Just double click on the file, and we will have the show on the screen. To save a file as PowerPoint Show, select this alternative under Save as type option in Save As dialog box (Figure 5.7). To open the Save As dialog box, click on File → Save As.
However, to run the slide show as described above, we will need to have the presentation program in the system. What happens if we take this presentation file to a machine which doesn’t have a presentation program loaded? Can we run the program?
5.8.1 Slide Designs
Now let us learn how to apply Designs to the slides to make them more attractive.
A slide design determines the background colour and picture as well as the colour and type of text on it. Follow steps given below to apply slide design to the templates :
- Click on the Slide Design option under the format menu. This will show the Slide Design task bar as shown in figure 5.8.

- Click on any design of the choice in the task pane. This applies the selected design to all slides of the presentation.
- If we wish to apply the design to selected slide(s) of the presentation, select the slide(s) from Slide Sorter pane. Now, click on the arrow which appears when we move the mouse to the desired design in the Slide.
- Design task pane, and click on Apply to Selected Slides from the resulting menu.
- Run the slide show once more to see the effect.
5.8.2 Custom Animation/Animation Schemes
We can animate text, graphics, diagrams, charts, and other objects on the slides by following these steps:
- Select the object.
- Click on Slide show Menu and choose option Custom animation.
- Click on the effects tab to apply the appropriate effect.
- We will see numbers like 1, 2, 3 appearing against the paragraph/objects – this is the order in which they will appear during the slide show.
- Repeat the process to apply animation for another instance, say this time for exit (instead of Entrance).
- Once again, we will need to run the slide show to see the effect. Click on
![2802.png]() at the bottom of Custom Animation task pane.
at the bottom of Custom Animation task pane. - We might have to click the mouse to move from one animation to another.
5.8.3 Slide Transitions…
While animation decides how each item in the slide emerges on the screen, slide transition takes care of how the slides (and not the items on the slide) appear one after the other during the show. We can apply a particular slide transition to all the slides or to some selected slide(s).
To apply slide transitions to the presentation,
- Open the presentation.
- Click on Slide Show and select Slide Transition to see the options in the task pane (Figure 5.9).
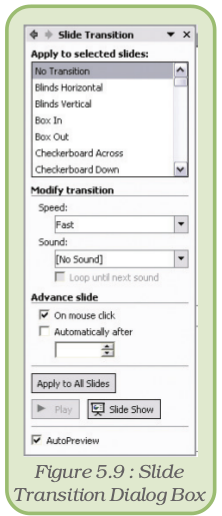
- If we want to apply it to some selected slide(s), select the slide(s) from Slide Sorter pane. To try out, just select the second slide of the presentation.
- Select the desired transition effect like Blinds Horizontal, Box In, Cover Down, etc. from the task pane.
- If we wish, we can change the speed of transition (options are slow, medium, fast).
Select medium. This option is available under Modify transition in task pane.
- In addition we can add sound that will be heard during slide transition. This option is also available under Modify transition in task pane.
- We can set the slide to advance on a mouse click, or automatically after a pre-decided delay. Select automatically and set the value to 00:11.
- Click on
![2807.png]() at the bottom of the task pane to see the effect.
at the bottom of the task pane to see the effect. - If we wish to apply the selected transition to all slides in the presentation, click on Apply to All Slides button else click on Apply.
5.8.4 Inserting Sound/Movies…
Most presentation software allows us to enhance the presentation by inserting sound and movies. In Microsoft PowerPoint, we can add them through following steps:
- Click Insert menu
- Select Movies and Sounds. We can add them using Clip Organiser or directly from file (Figure 5.10).

If we select the Clip Organiser option, we will see a selection in task pane very similar to the one we had seen in case of inserting clip art. Choose the desired movie or sound clip, and we will have it on the slide.
The other option is to get the movie or sound from file. If we select these options, we will see Insert Movie or Insert Sound dialog box, one very similar to the Save As dialog box. Select the movie or sound file that we wish to insert.
5.8.5 Navigation Between Different Slides Using Hyperlinks
A hyperlink is a connection from one slide to another or a connection to a web page, or a file.
A hyperlinked object may be a text, a graphic or an action button (a readymade button) placed on a slide, which when clicked, opens the connection (another slide, web page, file) the hyperlink was pointing to.
When we point to a hyperlink, the pointer takes the shape of a pointed finger (), indicating that it is something we can click on.
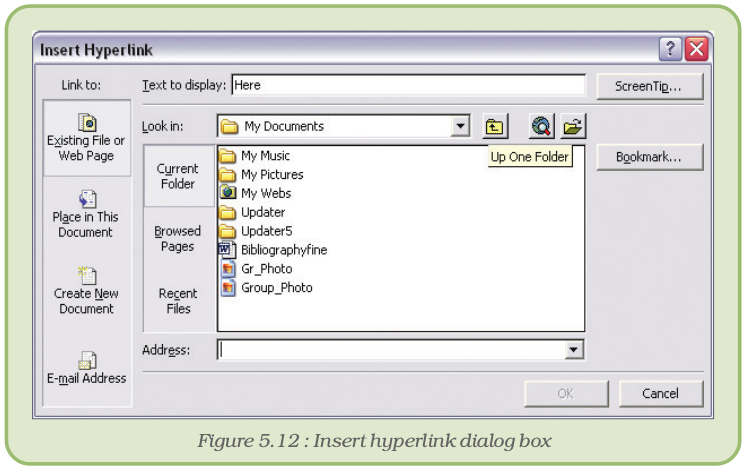
To create a hyperlink, first select the text or object that we want or represent the hyperlink with (for example, in figure 5.11 it is the word here). Click on Hyperlink from Insert menu. The Insert Hyperlink dialog box (Figure 5.12) opens up and we can browse for the file that we want to link as shown below:

If we want to create a link to another slide of the same show, then
- Select ‘Place in This Document’ on the left pane of Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
- We will see that all the slides of the presentation are listed in the dialog box.
- From this list, we select the slide we want to go to and click on OK.
If we want to create a link to another slide in a different presentation, then
- Click on Existing File or Web Page.
- Navigate to the correct folder and select the presentation to which we want to create the link.
- Click OK.
Similarly, we can make a hyperlink to a web page by giving its URL in the Address bar. For example to link to www.gmail.com, type http://www.gmail.com in address bar (Figure 5.13).

5.8.6 Adding Action Buttons
To insert an Action Button on the slide,
- Select the slide we want to place the button on.
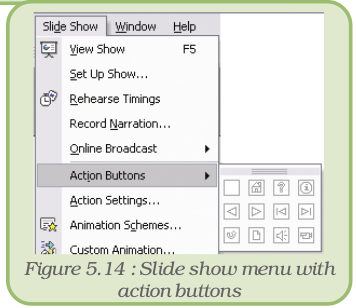
- On the Slide Show menu, click on Action Buttons option and select the button we want from the resulting cascading menu (Figure 5.14).
- Click on the desired location on the slide, and we will see the selected Action Button getting placed there, which can be later resized to suit the requirement. Additionally, the Action Settings dialog box (Figure 5.15) opens up.

- Select the Hyperlink to option and select the desired link from the drop down list box.
- Click on OK to complete the process.
If we plan to insert the same Action Button on all slides of the presentation, click on Master on the View menu. Select Slide Master. Now place the button on this Slide Master as in the previous steps.
5.8.7 AutoShapes
AutoShapes can be used to emphasise certain points in the presentation. These are available on the Drawing toolbar. They include several categories of shapes: lines, connectors, basic shapes, flowchart elements, stars and banners and callouts. These can be resized, rotated, flipped, coloured and combined to make more complex shapes. We can also add text to these shapes which then becomes part of the shape.
Follow the steps given below to draw an autoshape:
- Click on AutoShapes option on the Drawing toolbar
- Select the desired shape (Figure 5.16),
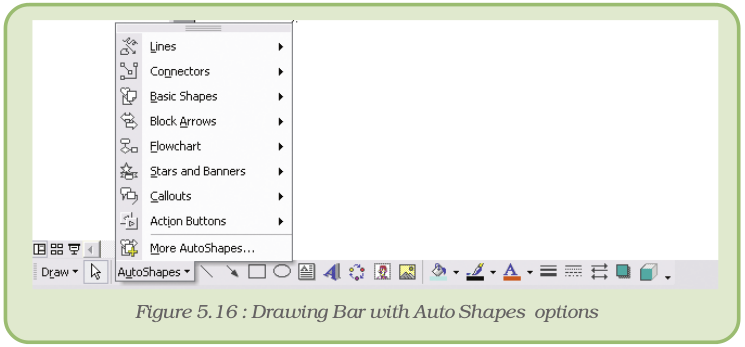
- Click and drag on the slide to draw the shape of desired size.
The handles (Figure 5.17) around a selected shape have the following purposes:
- The Sizing handles are the white handles around the shape which are used to change the size of the shape.
- The Adjustment handle is a yellow-diamond shaped handle. This handle, if present, indicates that the shape is adjustable.
- The Rotating handle is the green handle which can be used to adjust the angle of rotation of the shape.

A shape could have graphic attributes such as fill, line, and shadow or text attributes such as style, font, colour, and shadow. To put text into the autoshape, select the autoshape and just type in the desired text; and we will see the text appearing within the autoshape. If some text is already there, the new text typed will be appended to the exisiting text.
Tools for changing the basic attributes of a shape - fill color  , line color
, line color  line style
line style  (which decides on the thickness of the border), dash style
(which decides on the thickness of the border), dash style  (which decides whether the border line will be solid, dashed, dotted, etc.), shadow style
(which decides whether the border line will be solid, dashed, dotted, etc.), shadow style  , 3-D style
, 3-D style  and font color
and font color  are located on the Drawing toolbar. For changing the attributes, we need to select the autoshape that we have placed, click on the appropriate tool on the Drawing toolbar, and select the desired option. If we want to change the text attributes other than font color, select the autoshape and click on Font option under the Format menu to set the desired text attributes.
are located on the Drawing toolbar. For changing the attributes, we need to select the autoshape that we have placed, click on the appropriate tool on the Drawing toolbar, and select the desired option. If we want to change the text attributes other than font color, select the autoshape and click on Font option under the Format menu to set the desired text attributes.
5.9 How to Run a Presentation from a
Computer Not Having the Presentation
Software Installed?
When we want to Run a Presentation program from a computer not having the presentation software installed then Pack and Go is the way to do this which is described in Appendix 5.4.
Summary
- An electronic presentation program is a computer software that is used to display information.
- A presentation can have several slides, which can be displayed one after another.
- The places on the slide where we can click and type text for the presentation are called placeholders.
- The font, size, alignment, etc. will be same as that of the placeholder text, unless we change them.
- We can select the layout of a slide by selecting appropriate choice from Slide Layout task pane.
- A slide can contain non-text content too, like – chart, clip art, media clips, etc.
- We can apply formatting to the text in the slide – we can change the fonts and their associated features; we can apply bullets or numbers; and we can decide on the paragraph alignments.
- We can copy or move the content of a slide, or even the slide itself.
- There are three views – normal view to design presentation, slide sorter view to arrange the order in which slides will appear, and finally the Slide Show view is used while delivering the talk.
- If we don’t like the way our slides look, we can use Slide Design to improve them. We can apply a slide design to selected slides, or to all slides in the presentation.
- The way various items appear on the slide during a slide show is decided by the Animation that is applied. We can select preset animation schemes, or decide on our own using custom animation option.
- Apart from the items in the slide, we can control the way the slide itself appears during the slide show. This is done using slide transitions facility.
- Instead of listing out raw data, we can insert a chart in the presentation to make the data more meaningful to the audience.
- We can create hyperlinks on slides to connect it to other slides in the same or different presentation, or even to a file or a website.
- To facilitate navigation from one slide to another, we can include action buttons in our slides.
- AutoShapes can be used to get the audience’s attention to certain points in the presentation.
- A presentation file can be made to run on a computer system not having the presentation software (Pack and Go).
Exercises
Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is meant by slide design?
2. What is meant by animation schemes?
3. How do you change the bullets appearing in your presentation?
4. What are the three major functions of a presentation program?
5. What are placeholders?
6. What do you mean by Pack and Go?
7. What do you mean by slide transition?
Long Answer Type Questions
1. How can a transition help in your presentation?
2. What are the different ‘views’ in the presentation package that you are familiar with?
4. Discuss the process of inserting clip art into a slide.
5. List out the process of creating a hyperlink to connect to a slide in another presentation.
6. What is an AutoShape? Discuss the formatting that can be applied to an AutoShape.
7. How is a file saved as type Presentation different from the one saved as type PowerPoint Show?
10. How can we insert clip art in a slide? Explain.
11. How can we hyperlink a slide? Explain.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. The presentation is seen on the computer or a projection screen in the form of
(i) Slides
(ii) Pages
iii) Papers
(iv) Handouts
2. Animation decides the way
(i) the slides appear
(ii) the items in the slide appear
(iii) the text looks
(iv) the slides look
3. The first slide of presentation
(i) always has the layout – Title slide
(ii) normally has the layout – Title slide, but can be changed using Slide Layout task pane.
(iii) normally has the layout – Title slide, but can be changed using Slide Design task pane.
(iv) normally has the layout – Title slide, but can be changed using Slide transition task pane.
4. While working with AutoShapes, you can change the style of the text using
(i) Font Color
(ii) Line Style
(iii) Select Font from Format menu
(iv) None of the above
Activities
1. Design a presentation to make your friends interested in the book that you have read recently. Ensure that you use animation and slide transitions. Use AutoShapes to design an appropriate callout in the first slide.
2. Design a presentation on your favourite singer. Ensure that you include some of his/her music in your presentation. Place a hyperlink to link to some websites mentioning his/her achievements.
3. Prepare a presentation of your hobbies like playing cricket, listening to songs, gardening, photography etc.
4. Create a family magazine containing description of your family members, their role in the family and their photographs.
5. Prepare a presentation of your school with the following contents:
a. On the first slide, put the name and a photograph of your school.
b. On the second page, display the features of your school.
c. On the third page, put information about the library with a photograph.
d. On the fourth page, Science lab
e. And so on.
6. Suppose you are a student of class XI D and have been asked to prepare a slide show of new inventions of computer hardware. Collect latest pictures from the Internet and put them on different slides and also display their features with them.
Appendices
Appendix 5.1 : Text Layout Options
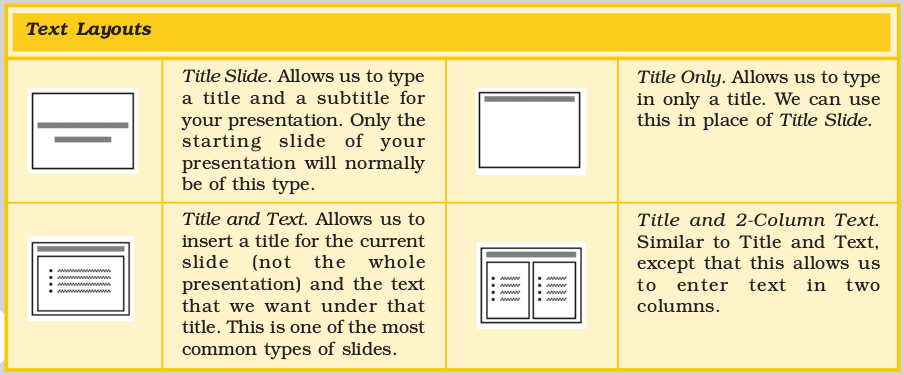
Appendix 5.2 : Content Layout Options

Appendix 5.3 : Text and Content Layout Options

 , and lastly on
, and lastly on
 . If we are not sure, just click on
. If we are not sure, just click on  without typing in any text.
without typing in any text. . Click on Sheet1 and feed in the data for the chart as we had done in the spreadsheet.
. Click on Sheet1 and feed in the data for the chart as we had done in the spreadsheet. Duplicate Slide.
Duplicate Slide. at the bottom of Custom Animation task pane.
at the bottom of Custom Animation task pane. at the bottom of the task pane to see the effect.
at the bottom of the task pane to see the effect.