Table of Contents
12
CCT Projects in Local Context
Objectives
After completing this Chapter, the student will be able to:
- understand the meaning of e-Governance,
- describe National e-Governance Plan (NeGP),
- recognise the relevance of e-Governance from the governance point of view,
- comprehend the architecture of e-Governance,
- appreciate the evolution of e-Governance practices in India and
- identify some of the Government’s e-Governance initiatives in local context.
“Three years ago India was emerging as an IT superpower. Today, the country is handling the most sophisticated projects in the world”
- Bill Gates, 30 July 2004
Introduction
There are several services provided by the government to solve our day-to-day problems. With the growth of CCT the government has taken steps to use various computer communication tools and technology to modernise its working. It helps in providing the services more conveniently and a means for the public to easily avail these services. This affects the service provider (Government) and the recipient (the citizen) both. Most of these projects are driven by local needs to exploit CCT for better services, efficiency and transparency. Various state governments have implemented projects with reference to the local context.
This chapter will provide exposure to various initiatives taken by the government in implementing projects covering various aspects of our society.
12.1 Need for e-Governance
An organisation, be it government or private, will be left out of the race if it does not keep pace with the major global shifts towards increased deployment of IT. In a fast moving world, the expectations of clientele will be naturally least tolerant to undue delays. Thus to sustain and survive, it is imperative for any organisation to reach out to its clientele and adapt to the changing paradigms by using technology. In any country, its government is a major service provider and answerable to its citizens in reaching out the benefits of its vast resources to them. The government’s various initiatives in becoming techno-savvy constitute various components of e-Governance.
12.2 Definition of e-Governance
e-Governance refers to the application of CCT to enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, transparency and accountability of informational and transactional exchanges at all levels. These exchanges can be :
- within the government, i.e. between government and government agencies of National, State, Municipal and Local levels,
- between citizen(s) and government.
The aim of e-Governance is to empower citizens through access and use of information.
12.3 Expectations from e-Governance
The services provided via e-Governance should be sustainable to cover all the segments of a society, at an affordable cost and customised to the local requirements. The services delivered by them should be reliable, authenticated, and timely, in a format and mode that is convenient to the users. It is estimated to provide complete services to meet the purpose.
m-Governance is the future of e-Governance services delivery, which will ensure inevitability and accessibility of e-governance services anytime, anywhere using mobile devices laptops, palmtops, mobile phones etc.
12.4 Government’s Initiatives
12.4.1 e-GOVERNANCE PROJECTS
Mostly, e-Governance projects are designed with various objectives such as providing easy access, extending access to un-served groups, introducing transparency, simplifying transaction procedures, minimising cost to citizens and to the government, increasing the government revenue, reducing the transaction time, offering new services, modernisation/adoption of best practices.
Implementation of these projects makes lives of common man better through technology implementation at national level in central government, at state level governments, at district level and finally at the village level.
National e-Governance Plan (NeGP)
The NeGP plan (2003-2007) was formulated by the Department of Information Technology (DIT), Ministry of Communications and Information Technology, Government of India to initiate and provide for long term growth of e-Governance in our country with the following vision :
“Make all Government services accessible to the common man in his locality, through common service delivery outlets and ensure efficiency, transparency and reliability of such services at affordable costs to realise the basic needs of the common man.”
NeGP aims to change and improve drastically the way in which the Government provides services to its citizens and empowers them to demand convenient, cost effective and transparent services.
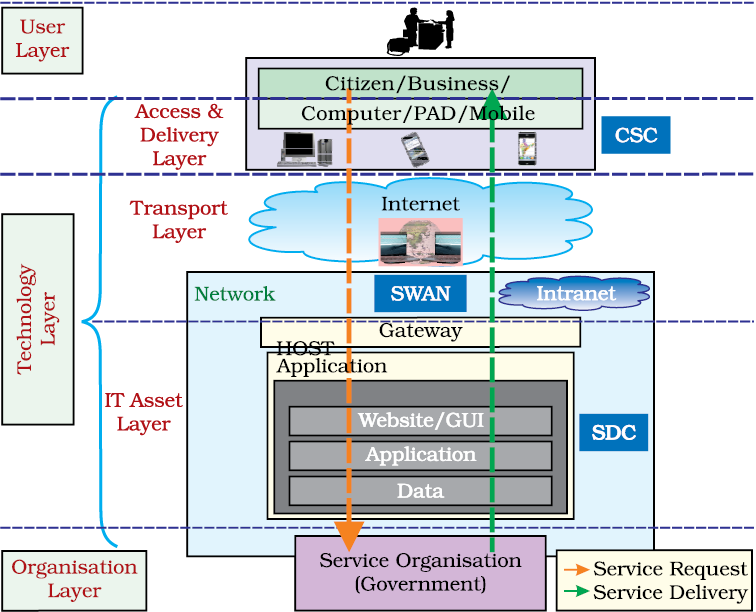
Figure 12.1 : e-Governance architecture under NeGP Source: DIT, Ministry of Communication and Information Technology
The architecture of NeGP consists of three layers: Organisation layer, Technology layer and User layer. The sharable infrastructure under NeGP is :
(a) Common Services Centres (CSCs) to facilitate services delivery electronically at the grass root level
(b) State Wide Area Networks (SWANs)
(c) State Data Centres (SDCs)
Technology Development for Indian Languages (TDIL)
Ministry of Information technology has taken initiative to start the TDIL programme. The aim of this programme is to develop and promote the use of Information processing tools and techniques for Indian Languages. Some of the objectives of the programme are to :
- facilitate human-machine interaction in Indian languages and multilingual knowledge resources.
- consolidate technologies developed for Indian Languages and integrate them to develop innovative user products and services like Multi-lingual Dictionaries, Encyclopedia, Gyan-nidhi Creative Writing System, Translation Support Systems, Text-to-speech and Speech Recognition System, Pocket Translator, Reading machine for the blind and the deaf portals.
- provide requisite technology development and bridging the existing technology gap in the Hindi speaking states of India.
12.4.2 e-GOVERNANCE PROJECTS IN LOCAL CONTEXT
There are several projects existing in different states in regional languages. The goal behind these projects is to make various public services and schemes available through technologies to a common man in their own understandable language. Through these IT based projects government tries to ensure the following:
- Enhancing awareness of IT enabled services
- Improving IT penetration
- Localised solutions
- Availability of IT learning material in local language
- Standardisation
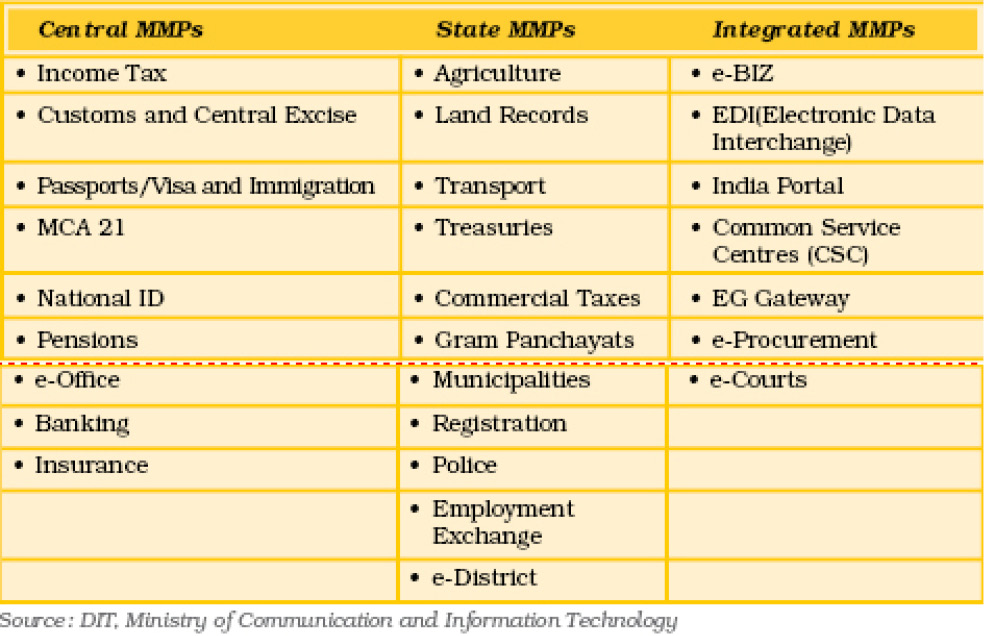
12.4.3 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs)
NeGP implements a significant number of Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) and various projects at the central and state government level.
12.5 APPLICATION AREAS OF E-GOVERNANCE
Some of the departments and services where e-governance is applied are:
- Public Grievances : Electricity, Water, Telephone, Ration Card, Sanitation, Public Transport, Police.
- Rural Services : Land Records, Below Poverty Line (BPL)/Economically Weaker Section (EWS) Families.
- Police : FIR Registration, Lost and Found valuables and persons.
- Social Services : Pension, Old Age, Widows, Ex-gratia Scheme, Acquisition/Rehabilitation and Compensation, Registration of Licences and Certificates, Ration Card, Birth Certificate, Death Certificate, Domicile Certificate, Caste/Tribe Certificate, Arms Renewal, Registration of Documents, School Registration, University Registration, Motor Vehicle Registration, Driving License.
- Public Information : Employment Exchange Registration, Employment Opportunities, Examination Results, Hospital Availability/Services, Railway Time Tables, Airline Time Tables, Road Transport Time Tables, Charitable Trusts, Government Notifications, Government Forms, Government Schemes.
- NEWS Services : Civil supplies, Old Age Pension, Widow Pension, Handicapped Pension/Services, Ex Gratia Payment.
- Agriculture Sector : Speeds Information, Pesticides, Fertilisers, Crop disease, Weather Forecast – short range/District wise, Market Price.
- Utility Payments/Billing : Electricity, Water, Telephone.
- Commercial : Taxation and Return Filing, Income Tax, Corporate Tax, Custom Duty, Central/State Excise Duty, Sales Tax, House Tax, Property Tax, Octroi, Road Tax, Company Returns.
- Government : Electronic Procurement, Education University Model for e-Governance.
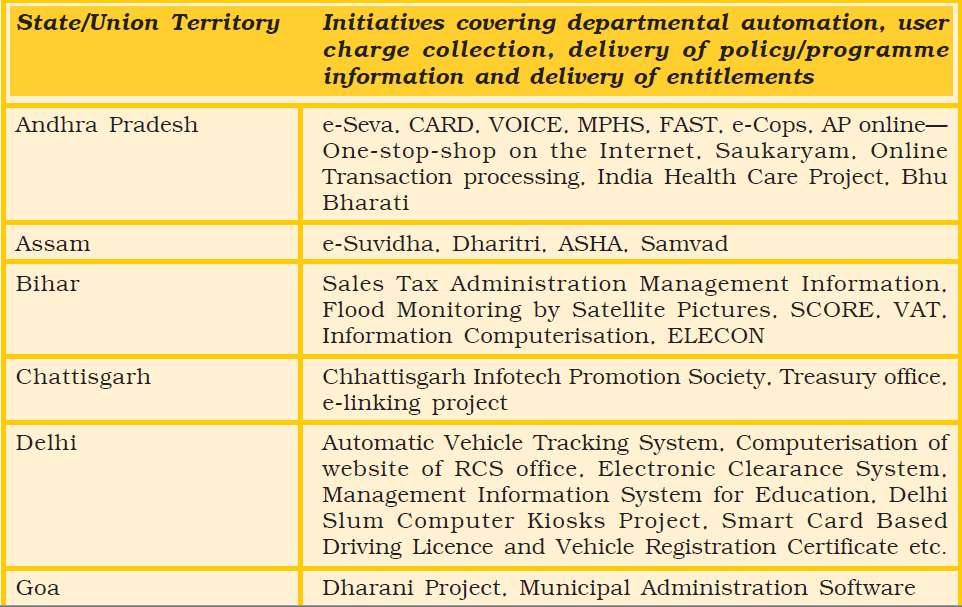
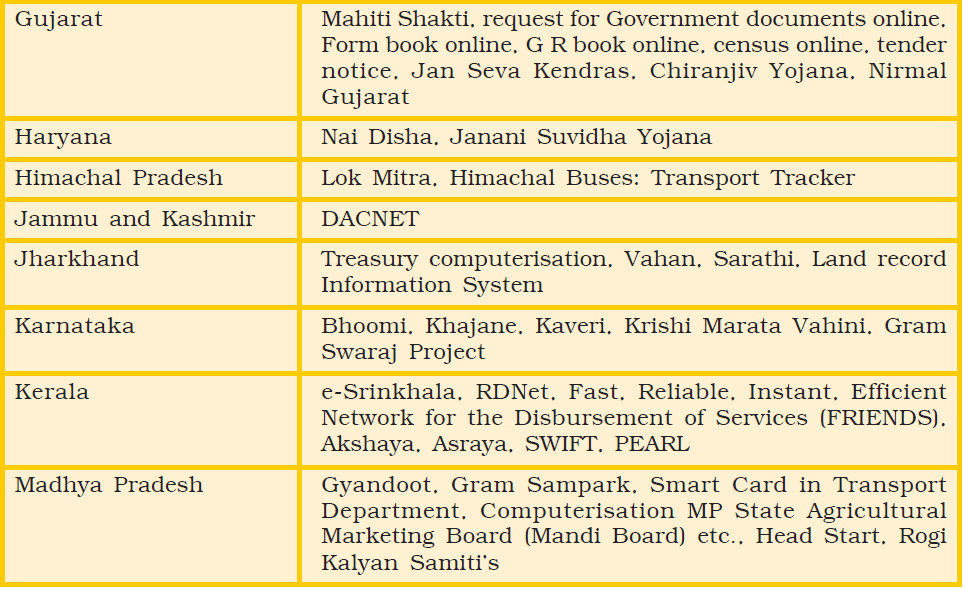
12.6 Implementation of Various project
Table 12.1 : Some of the projects implemented by various state governments
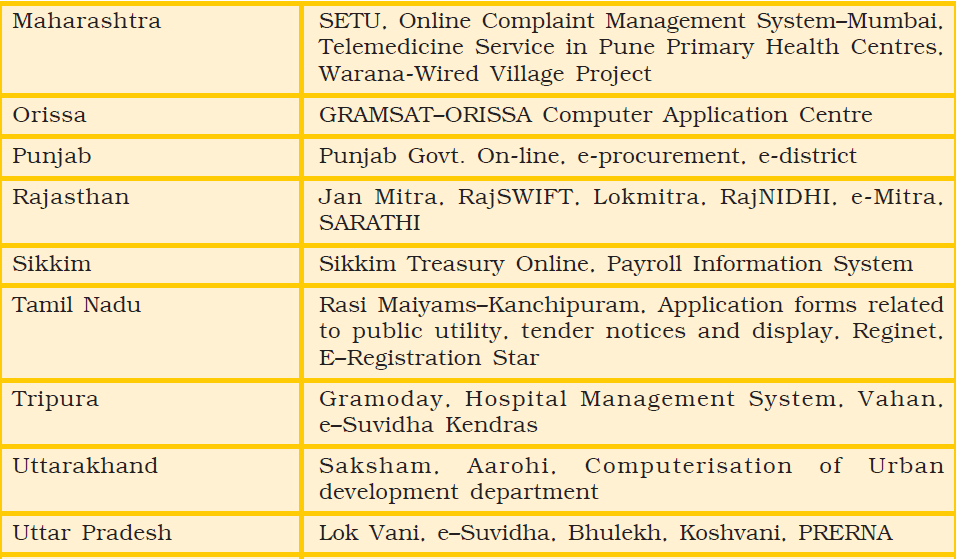
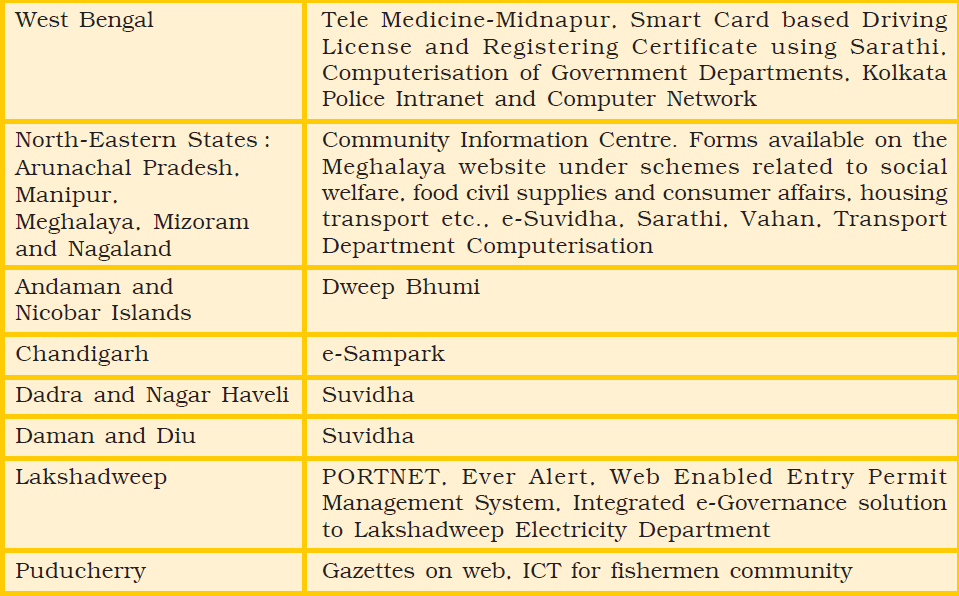
Summary
- With the advent of CCT, the Government of India has taken steps to use various technologies to modernise its functioning.
- Various State governments also have implemented e-Governance Projects in reference to local Contexts.
- e-Governance is the application of information and communication technologies to transform the efficiency, effectiveness, transparency and accountability of informational and transactional exchanges.
- NeGP implements a number of Mission Mode Projects (MMP’s) both at the central and state levels to create a citizen-oriented environment for e-Governance.
- TDIL aims at promoting the use of IT tools for providing services in Regional Indian languages.
- The goal behind projects in local context is to make various public services and schemes available to common man in their own understandable language.
EXERCISES
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Define e–Governance.
2. What is the need for e–Governance?
3. What is m–Governance?
4. Expand the following abbreviations:
- CSC
- NeGP
- SWAN
- SDC
- MMPs
5. Name some on-going e–Governance projects?
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What do you mean by e–Governance and what are its components?
2. Describe a few recent e–Governance projects implemented by your State/UT government?
3. What are the recent initiatives taken by government for implementing
e–governance?
4. Elaborate the application areas/departments in which e-Governance can be applied.
5. What are the expectations of recipients from the services delivered by
m–Governance?
6. Explain NeGP architecture with the help of a diagram.
7. Describe some initiatives taken by Government to promote CCT tools in Indian languages.
8. Discuss the applications of e–Governance Projects in local context with examples.