Table of Contents
Chapter 10
CAMPAIGN DESIGN

Campaign is typically a military term used for a well organised course or a series of action. It means strategic planning for all round action as was done for a war, taking into account attacks on surface, from air and sea, by the army, air-force and navy. Similarly, in an advertising campaign a
multi dimensional strategy is planned by using different media.
Design for an Advertising Campaign is not only to create a beautiful layout for the sake of aesthetics or creativity, it should also be useful. It usually is well planned and designed after deep thought and thorough brain storming sessions into a functional organic unity of copy, typography, illustration symbol, product. Design as a whole, all elements should be integrally related to each woven into a theme, one related to the other to convey the message.
The different advertisement layouts of a campaign must be harmonious and clarify the purpose and expression of an idea through its execution. All the aspects of the campaign, A to Z must be taken into consideration. Apart from the function and method of production, the idea is of course important for an effective and desired result. The idea is abstract, it should be given a theme to make it result oriented so that people should respond to it, sales must go up. Only then the design of a campaign is considered successful. The creative group working on the campaign tries to resolve things by first understanding the purpose of the advertising
This may be:
• to introduce and launch a new product or service.
• to get the product used in place of the competitor’s.
• to increase the frequency of use.
• to create a new long term habit.
• to arouse interest and provide technical information.
• to obtain seasonal sales where appropriate (cough syrups, air conditioners, room heaters etc.)
• to impress the retail trade.
Only after this, an advertising campaign is designed.
“Advertising strategy is designed to support adequately the marketing strategy when translated into a plan of action is known as campaign planning in advertising.”
-(Dr. G.M. Rege: Advertising Art and Ideas)
Kinds of Campaigns
Campaigns are designed with different reasons and objectives. The main two kinds are Product Promotion and the other kinds are where there is no product but a service or idea or just a message. We will see them in detail to understand the difference.

Product Promotion
It is obvious that a product has to be sold and that is the prime and ultimate goal. However the planning and approach in designing a campaign for different types of products is different. Campaigns for fast moving consumer good (FMCG) like toiletries, snacks beverages etc. usually will have consistency all round the year. They may also come up with different and creative advertisements to attract new consumers and retain old ones.
For consumer durable products the marketing policy in general terms may be completely different like:
• to encourage purchasers actively looking for the product to buy one particular make.
• to encourage purchasers to replace obsolete models.
• to widen the market for the products.
From the media point of view, advertising such products calls for a fair amount of descriptive copy, which in turn means large spaces. For mass-consumer products, to need to keep the product’s name in front of the consumer is vital, and continuity of advertising is essential to combat competition.


Non-Product
As the name suggests, these campaigns do not promote any product. They are for advertising and promoting Services and Businesses called Corporate Campaigns.
Corporate Campaigns
Companies like people have a personality of their own. They make an impact and leave impressions on people who come across them. Every organisation needs to create and build its personality or image. Here image means reputation. The foundations of this image are made of the Moral, Aesthetic, Intellectual and Social values. These values become habits and get woven into the culture of an organisation and reflect in business practices through character, psychology and identity. They are also instrumental in the company’s success.
The projection of these intrinsic values become important when a company floats a public issue to raise its market equity. This means the company looks out for financial investment in the company by way of selling its shares to citizens. It is at such a time that the reputation or image of the company needs to be good, strong and stable in the minds of public. To create this positive and favourable image, corporates usually launch an advertising campaign high-lighting their ideology and strengths. The campaign could be centered on themes like Organisation Culture (character) or Organisation Identity (perception). Apart from businesses, political parties also create an image about their vision and mission for society and publicise their manifestoes.

A set of stationery
Service Campaigns
These Campaigns create awareness, inform and promote services offered by any organisation like the Indian Railways, Airlines, Hotels, Hospitals and Income Tax Department, Postal or Courier services and many others like them. They could belong to the State or could be placed by private parties.
Social Awareness
These campaigns are designed to create Social awareness for the upliftment and betterment of our society. These could be released by the State authorities or Non Governmental Organisation, popularly known as NGOs. These could be projecting our Constitutional and Civil Rights, Education, Health, Right to Information (RTI), Consumer Awareness and Social evils like Illiteracy, Dowry, Female Foeticide, Drug abuse, Ragging etc.


Activity 1
Identify a few social awareness campaigns in print media and electronic media and study them.
Planning a Campaign
In order for Advertising to be effective and impact creating it needs to be attractive, different, refreshing and that can be only achieved through creative thinking. There are no set rules or formulas established in creativity and campaign planning. In the advertising business the work of copy writers, art directors, print and broadcast producers, film and T.V. directors – is generally referred to as the creative side of advertising and their inputs help plan a campaign after the research figures are studied.
There are different stages of the creative process in planning a campaign, first comes brain storming, ideas and visualisations. This includes:
• Gathering of raw materials – for our immediate need and materials which come from a constant enrichment of our general knowledge.
• The working over of these materials in our mind.
• The incubation stage is where you deal with something motivating and it can be dealt in different ways – humour, sympathy, anxiety, fear etc.
One of the ways of planning an effective campaign is visualising precisely by a pictorial dramatisation – the approach can be either direct or indirect, depending on need of the advertiser. Creative planning decides on the basic theme while execution includes meticulous planning of how the story may be told in the best possible manner.

When all these factors have been decided, the media planner and the creative group together will make the final decision as to which medium to recommend. The allocated budget also needs to be considered, the size and frequency will depend on this.
Eventually there is an analytical study and a hypothesis is reached about the success of the campaign.
Brain Storming
Brain storming is a session, when all the big officials sit and discuss an issue to get new ideas.
The ideas are generally used for headlines. This is collective work–like a panel discussion of 8-10 people. Here all ideas are accepted without any criticism with an open mind, the quantity, the quality and the variety of combinations are analysed thoroughly.
Working on a Campaign
The basic objectives of advertising are to hold buyers or consumers, to create new consumers and the third is to attract and convert competitor’s buyers towards self. Other possible objectives could be to inform about or introduce a new product or service. Or suggest a new use of a product, to remind and persuade. The client usually is clear about the objective, the campaign is planned. Advertising campaigns differ in strategy, hence the creative approach too differs. Three steps to develop a creative strategy based on the research would help in;
Message Generation = source, resource, data, media
Message Evaluation = selection, action, production
Message Execution = release, frequency, exposure.
While planning a strategy for a campaign—
• First write the Unique Selling Points (USP) of the product or service.
• List out how a buyer stands to benefit.
• Next decide the consumer profile called the demographics like age, sex, education, income, occupation etc.
• After that list out psychographics your campaign should aim to establish like lifestyle, attitude, personality traits, style etc. With these details clearly in order the rest of the planning can take place in collaboration with the creative teams.
Did you know?
If a prospective consumer identifies himself or herself with the model in the advertisement shown using or endorsing the product, he or she is most likely to buy the product.

Research and Data Collection
The role of Research is primarily to explore the nature of image the company and its products or services carry in the market or in the minds of consumers vis-à-vis the image of competitors and or competitive products, their reputation, range, prices and take corrective steps if required while planning and launching a new advertising campaign. Every opportunity and method of gathering opinions of other people, and the chance of learning something about the company’s image should be seized. Then the advertising must be planned accordingly to impress the readers and answer any doubts before they are formulated in the minds of readers who could be the customers.
It also helps understand, fashion, trends, demands, requirements, buying motives and buying patterns of the consumers. It then provides data to understand the geographical demands or requirements and plan the campaign’s approach theme to match the needs and expectations of prospective consumers. Research is carried out in three areas that of the general market trends, competitive and similar products in the segment and the psychology of the consumers. Finally it assists in measuring the success of communication aspects of the campaign in reinforcing or correcting the image
Market Research
A scrutiny of the market is of prime importance for the advertiser. These days advertising agencies provide this service. This study helps understand the trends and demands of the market. It is then easy to design the campaign in a manner to fulfill this demand.
When the proposed advertising is intended to create a market, or when it is planned to launch a new product rather than to increase the demand for one already known, one must formulate the ‘consumer profile’ by research and imagination. In short, one must study the prospective ‘market’.
It is also necessary to study the marketing policy, pricing, and the channels of distribution of the competitors. Ideally one should make four separate and comprehensive studies to have a clear understanding of:
1. the sales potential of the product;
2. the actual and/or potential market;
3. the methods and market of competitors; and
4. the selling policy.

If a product is meant for children then an attempt is made that the advertisement style should appeal to that segment
Consumer Research
This is conducted to understand the needs of the consumers and to match buying motives and use ideas that appeal to the prospective consumers. How the given segment of prospective buyers perceive the product at hand. The matching appeal will thus be used in the campaign. There are primary and secondary appeals which we will study later in this chapter. The consumers living in different geographical locations could perceive a product differently, or have different wants, culturally, seasonally or otherwise. Campaign planners need to be aware of and sensitive to while designing the approach.
If there is a regular demand for the product already, then the purpose of the proposed advertising would be to maintain or increase it, in which case the data collector should talk with actual customers so as to learn the type of persons to whom the goods appeal, their habits and levels of satisfaction. One could get suggestions for improvement like demand to introduce a new flavour or size, maybe even complaints, prejudices and opinions. The research could tell us their buying habits like bulk purchasing, monthly or seasonal etc. as well as their exposure to various media.
Product Research
Product research is done to collect data of all other products in this segment or price range. For example if we take detergent powders, the study will list out all the detergents available in the market. The packaging they are available in, their prices, demand and monthly sales, market share, how much expansion is expect? Also data should be collected on the specialties or USPs of all the products available like ‘lemon flavour’ or ‘special whitening agents’.
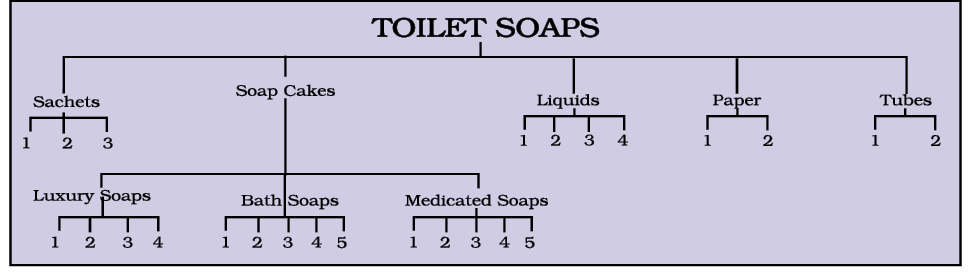
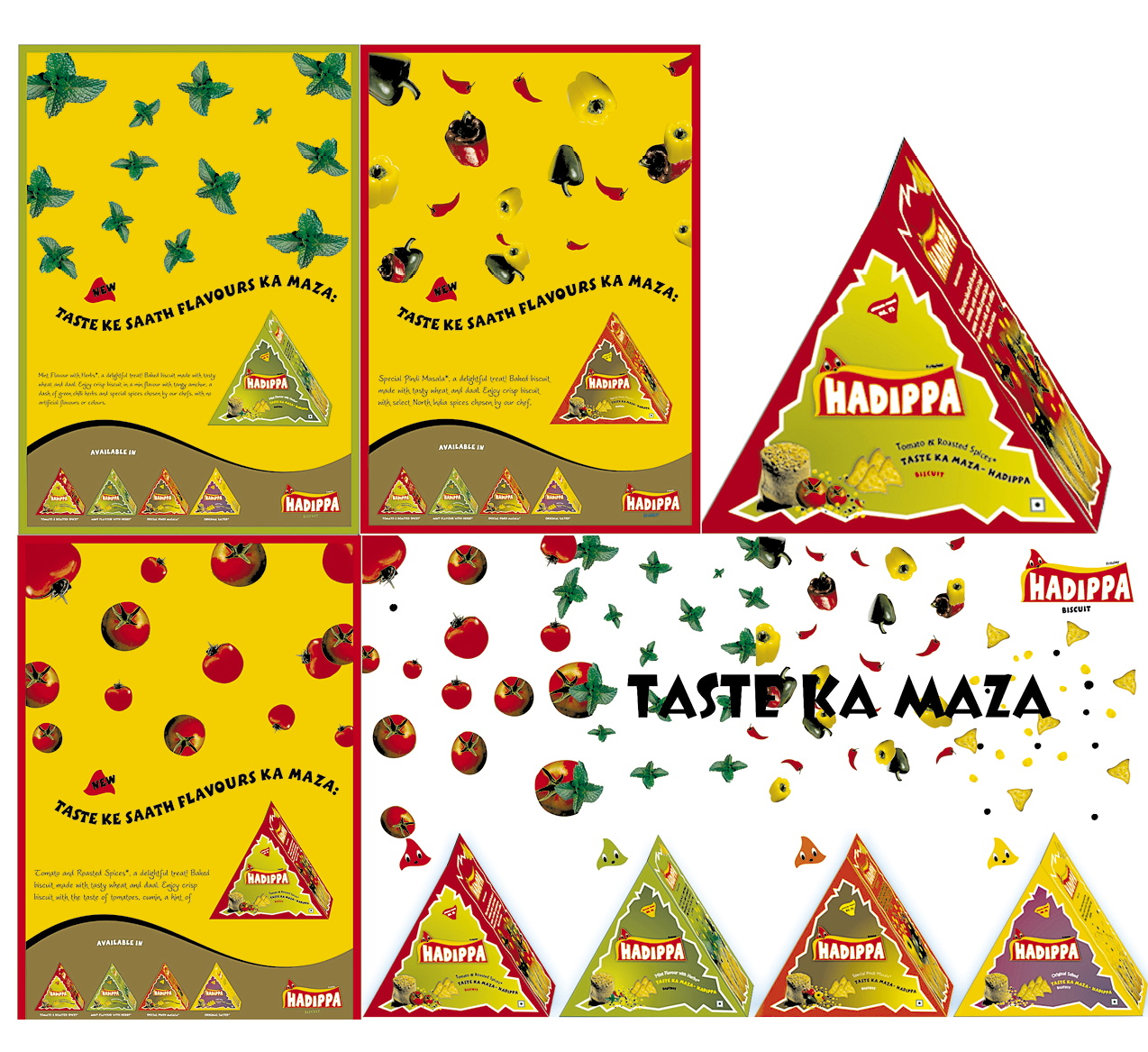
Product research is carried out for all the competitive brands that may fit into the range of the product the company proposes to launch. Shown here is a flow chart for toilet soap concentrating on soap cakes. Further to this, could be a survey of comparative prices, popularity index, consumer perceptions, choices and preferences like aroma, fragrance etc.
Creative Aspects
Idea is the result of subjective and objective thought. The end product should be the result of a creative idea, analysed, interpreted, developed and improvements made, all creatively coordinated well according to the theme. It must play upon the memory, instinct and intuition of the viewer or reader and stimulates the required reaction. So what actually is going into the making should be given due consideration. No doubt the layout should be attractive; it need not be loud and complicated. Remember there is a message to be delivered too. The whole approach is misunderstood if all it does is to create visual sensations alone. The concept should be simple and functional.
Illustration penetrates deep and replaces language so it must be powerful. An advertising design and idea is a device to make a message more interesting to the reader, to give it distinction and memorability. A creative advertising design is an interesting or unusual arrangement of the theme with other elements (logo, copy, symbol etc.). It has a definite function to perform, as the most important unit for any advertisement. If photography is used, its purpose is to illustrate a story in a more authentic and believable manner, true to life.
Colour is a very important factor in advertising because it attracts attention. If an advertising is colourful its obviously more attractive, provided it is used discriminatively. But before launching colour in advertising it is essential to understand colour preferences of the consumer, especially because colour has emotional qualities. Colour increases the legibility of the letter forms. Image some text in red on white, and then think of yellow text on a white background.
• Creativity in Words and Expressions, which provide Motivation to consumers and other public.
• Be effectively creative. Attract attention and invite reading.
• Always providing “To Buy” conditions.
This actually becomes the duty of the campaign designers to shape the correct and conducive approach and provide the required motivation to buy the product.


The Brief
This is usually a document the client gives or is expected to give to an advertising agency at the time of assigning the job and signing contract. The brief is meant to reduce the communication gap between the client and the agency. It spells out in details what the client actually expects to achieve from the campaign in terms of design and results. The brief provides an orientation and gives perspective for executing a campaign. However, while writing a brief the client should be as accurate as possible in listing out the expected goals keeping in mind the following:
| • Achievable | • Honest |
| • Meaningful | • Measurable criteria |
| • Finite by time | • Preferably phased out |
Developing a Concept
The central idea of any advertising campaign is to motivate action, thus the foremost is to present benefits that stand out. Once we know the reason a consumer buys something, we know how he expects to benefit when he buys something. So the copy should use that appeal very powerfully. The effective use of appeal is made when the advertiser successfully matches the selling points to the buying motives. Motives are “drives” that cause a human being to act in a certain way, in this case to buy.
Buying motives could be Social, Psychological, and Economical. There are some appeals like food, shelter and clothing which are basic, called primary appeals. Though these days we don’t see much of these in advertisements since society has developed. The use of secondary appeal is more common currently. These could be any of the following:
Security, Health, Comfort, Love, Fear, Ego, Status, Convenience, Pride, Fashion, Aesthetic, Pleasure, Economy, Profit, Beauty, Safety, Curiosity, Humour, or more than one used at a time.
Selecting the Appropriate Media
The media planner has the choice of spreading the campaign over 2 or 3 different media or putting all the efforts behind a single one. For this task there is a checklist.
• Does it achieve impact and penetration in terms of the message it has to deliver?
• Does it cover a reasonable percentage of the target market?
• Is the message appearing with sufficient frequency to influence choice at time of sale? In almost every case, there is one medium which will give a more positive answer to these questions than any other. The campaign therefore should be concentrated on achieving adequate coverage and frequency.
Before the media plan is made it is necessary to know the budget allocated for the task. The media planner then makes the best of what is set aside. Size of the campaign is dependent upon the creative requirement; and once a size is established, the length of the campaign and the selection of the media can be planned to minimise the wastage. Research shows that it takes at least three exposures for an advertisement to make an impact on a reader, and the campaign builds up coverage and penetration as it develops.
Activity 2
Collect some advertisement where primary and secondary appeals have been used.

Innovative way of attracting attention without actually showing any food product
Frequency of the appearance is also important. Media planners decide how often the customer should be exposed to the message.
This depends on the urgency of purpose where there is a time bound compaign, like in case of elections, sports and cultural events and health hazards like epidemics. For consumer durable products the marketing policy in general terms may be completely different. If there is seasonal selling like during festivals, campaigns are timed to break just before that period.
Departments of an Advertising Agency
Most advertising is handled in two ways: one is the regular advertising agency which works to advertise the products and services for anyone willing to pay. They handle all the research, design, execution and publicity for a client. The other are
in-house departments in big companies, they employ experts and other staff in their own advertising department. Some advertisers have their own advertising departments and also engage the services of outside advertising agencies to execute the bulk of their advertising work. The work is, however, distributed according to the capacity, and expertise of the advertising department to handle certain types of work only, the balance including creative planning and releasing through the major media is undertaken by advertising agencies.
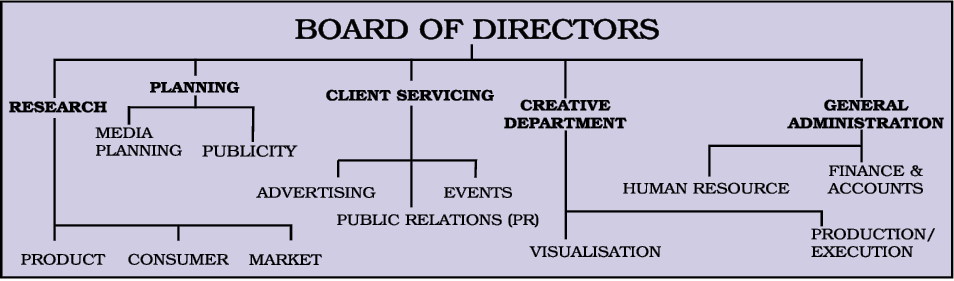
This is the conventional format of an advertising agency. However these days the structure may differ from organisation to organisation to suit their business environment. Newer departments like Online Communication and Healthcare are formed as separate business units to cater to niche sectors
Most agencies have different departments to handle the different aspects. The main sections usually are:
• Research Department, which looks after research and data collection of the markets, products and consumers. The research department analyses the data and give recommendations for launch of an advertising compaign.
• Planning: There is a ‘Plans Board’ and the team leader is the Managing Director. Under whose guidance different groups.
• The Media team takes care of planning, selection, budgeting, releases in print, electronic and other media. It also checks and documents the exposure.
• Publicity: One team of the planning group looks after the publicity of the agency itself. They look after growth and expansion of their own business as well.
• Client Servicing: In an advertising agency the group of people or the team working and coordinating with a client are called the account people, because a client or the company is known as an “account”. There is usually a different team working with different client or account, so that the client’s need can be understood and they can be catered to or serviced accordingly. Here the term account should not be confused with the people who look after billing and other financial matters. The team is headed by an Account Manager, however, an Account Executive is the most crucial link between the client and the agency.
• Advertising: Different clients have different requirements. Traditionally an advertising agency works only for advertising, so a major chunk of trained people take care of this segment and their team coordinate with the creative team forming the link between the client and the creative artists.
• PR and Events: All advertising agencies may not be undertaking Public Relation activities as these days there are specialised agencies for PR assignments, and some specialise only in events. But all advertising agencies have this section at least to take care of their own business development and marketing. They also have in-house events and celebrations which need to be organised well, as existing or prospective clients are also invited on such occasions.

A system like this is a part of any sound mixing studio where radio jingles and sound effects are created
• Creative team is headed by the Creative Director, with sub-groups for Art Direction, Copy Writing, Audio-Visual Scripting, Photography and all things related to the creative and aspects of design.
• Visualisation: The visualisation team is the one which actually generates ideas and work on the concept, theme, copy, visual etc. looking at pros and cons and options, before presenting the creatives to client. After the basic approval from the client they proceed with artworks and executing the assignment.

The creative or art department works to create concepts with which the target auudience can be attracted
• Production and Execution: As the term itself suggests looks after the production, offset and digital printing, fabrication and manufacture and installation of things designed by the art department. Could also be for advertisement in media, publicity with banners, posters other media and events.
• General Administration has its own General Manager who looks after all the administrative matters, be that accounting, sponsorships, partnerships, billing, salaries, banking budget allocation and other financial matters. The Human Resource people look after staff welfare, recruitment, training and human resource development. Even infrastructure development and purchase come under this department.
The In-house Advertising Department
The in-house advertising department is also headed by the advertising manager who is primarily a salesman; he must plan all work with sales as the ultimate aim. In a small concern, he may be the copywriter, layout artist, media man etc. too, while with larger firms, several people may be employed to carry out each of the special duties. Most importantly he must know his product well. He must see and test the product in use and compare it with competitive products, to know its plus points and weak points.
Did you know?
• In 1931 the first full-fledged Indian advertising agency was launched. Competition and demand were growing, trained personnel were sought for.
• In 1945 The Advertising Agencies Association of India was formed, introducing a code of conduct, and streamline media practices.
• 1952 The Indian Society of Advertisers was formed, to promote interest in advertising and raise its standard.
| BROAD MEDIA CLASSFICATION | VARIOUS MEDIA IN EACH CATEGORY | RESPONSIBLE PEOPLE | PRODUCTION PROCESS |
| | Newspapers Magazines Posters Point of Purchase Direct Mail Brochure etc. | Art Director Copy Writer Content Writer Graphic Designer Photographer Finishing Artist | Letter Press Printing Offset Printing Digital Printing Screen Printing
|
| Electronic | Radio Television Film and Cinema Internet | Art and Film Director Copy Writer Content Writer Web Designers | Digital Analog
|
| Outdoor | Hoardings Vehicle Graphics Bus Bays Neon Signs Balloons/Ambient Road Shows Events Exhibitions | Art Director Graphic Designer Architects Installation Designer
Anchor and Performers Space Designers Graphic Designers | Fabrication-Wood, Metal Mechanical Installation–Structural, Lighting, Sound Electrical Electronic–Projection, Laser Printed and Display Material Painting and Cladding Flooring |
Different areas of responsibilites within an advertising agency

An in-house studio needs to be well equipped with state-of-art infrastructure, reference library and conferencing facility
Exercise
1. Compare and contrast product campaign and non-product campaign.
2. List out the various objectives for designing an ad-campaign.
3. Make a list of people who would come under creative side of the advertising business.
4. What is the contribution of research to make a product or a service successful in the market?
5. What are the key considerations for the selection of media for an advertising campaign?
6. How is the role of a graphic designer working in an advertising agency different from a graphic designer working in the in-house advertising department of a corporate?