Find the domain of each of the following real function.
(i) 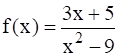
(ii) 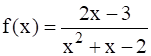
(iii) 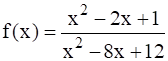
(iv) 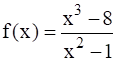
(i)
Given: ![]()
Need to find: Where the functions are defined.
To find the domain of the function f(x) we need to equate the denominator to 0.
Therefore,
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
It means that the denominator is zero when x = 3 and x = -3
So, the domain of the function is the set of all the real numbers except +3 and -3.
The domain of the function, Df(x) = (- ∞, -3) ∪ (-3, 3) ∪ (3, ∞).
(ii)
Given: ![]()
Need to find: Where the functions are defined.
To find the domain of the function f(x) we need to equate the denominator to 0.
Therefore,
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]() &
& ![]()
It means that the denominator is zero when x = 1 and x = -2
So, the domain of the function is the set of all the real numbers except 1 and -2.
The domain of the function, Df(x) = (- ∞, -2) ∪ (-2, 1) ∪ (1, ∞).
(iii)
Given: ![]()
Need to find: Where the functions are defined.
To find the domain of the function f(x) we need to equate the denominator to 0.
Therefore,
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]() &
& ![]()
It means that the denominator is zero when x = 2 and x = 6
So, the domain of the function is the set of all the real numbers except 2 and 6.
The domain of the function, Df(x) = (- ∞, 2) ∪ (2, 6) ∪ (6, ∞).
(iv)
Given: ![]()
Need to find: Where the functions are defined.
To find the domain of the function f(x) we need to equate the denominator to 0.
Therefore,
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
It means that the denominator is zero when x = -1 and x = 1
So, the domain of the function is the set of all the real numbers except -1 and +1.
The domain of the function, Df(x) = (- ∞, -1) ∪ (-1, 1) ∪ (1, ∞).