Solve each of the following in equations and represent the solution set on the number line.
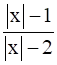 ≥ 0, x ϵ R. –{–2, 2}
≥ 0, x ϵ R. –{–2, 2}
Given:
![]() ≥ 0, x ϵ R. – {–2, 2}
≥ 0, x ϵ R. – {–2, 2}
Intervals of |x|:
x ≥ 0, |x| = x and x < 0, |x| = -x
Domain of ![]() ≥ 0
≥ 0
![]() is not defined for x = -2 and x = 2
is not defined for x = -2 and x = 2
Therefore, Domain: x < -2 or -2 < x < 2 or x > 2
Combining intervals with domain:
x<-2, -2<x<0, 0 ≤ x<2, x>2
For x < -2:
![]()
![]() ≥ 0
≥ 0
Signs of – x – 1:
-x -1 = 0 → x = -1
(Adding 1 to both the sides and then dividing by -1 on both the sides)
-x – 1> 0 → x < -1
(Adding 1 to both the sides and then multiplying by -1 on both the sides)
-x – 1 < 0 → x > -1
(Adding 1 to both the sides and then multiplying by -1 on both the sides)
Signs of – x – 2:
-x -2 = 0 → x = -2
(Adding 2 to both the sides and then dividing by -1 on both the sides)
-x – 2> 0 → x < -2
(Adding 2 to both the sides and then multiplying by -1 on both the sides)
-x – 2 < 0 → x > -2
(Adding 2 to both the sides and then multiplying by -1 on both the sides)
Intervals satisfying the required condition: ≥ 0
x < - 2 or x = -1 or x > -1
Merging overlapping intervals:
x < -2 or x ≥ -1
Combining the intervals:
x < -2 or x ≥ -1 and x < -2
Merging overlapping intervals:
x < -2
Similarly, for -2 < x < 0:
![]()
![]() ≥ 0
≥ 0
Therefore,
Intervals satisfying the required condition: ≥ 0
x < - 2 or x = -1 or x > -1
Merging overlapping intervals:
x < -2 or x ≥ -1
Combining the intervals:
x < -2 or x ≥ -1 and -2 < x < 0
Merging overlapping intervals:
-1 ≤ x < 0
For 0 ≤ x < 2,
![]()
![]() ≥ 0
≥ 0
Signs of x – 1:
x – 1 = 0 → x = 1(Adding 1 to both the sides)
x – 1 > 0 → x > 1(Adding 1 to both the sides)
x – 1 < 0 → x < 1(Adding 1 to both the sides)
Signs of x – 2:
x – 2 = 0 → x = 2(Adding 2 to both the sides)
x – 2 < 0 → x < 2(Adding 2 to both the sides)
x – 2 > 0 → x > 2(Adding 2 to both the sides)
At x = 2, ![]() is not defined
is not defined
Intervals satisfying the required condition: ≥ 0
x < 1 or x = 1 or x > 2
Merging overlapping intervals:
x ≤ 1 or x > 2
Combining the intervals:
x ≤ 1 or x > 2 and 0 ≤ x < 2
Merging overlapping intervals:
0 ≤ x ≤ 1
Similarly, for x > 2:
![]()
![]() ≥ 0
≥ 0
Therefore,
Intervals satisfying the required condition: ≥ 0
x < 1 or x = 1 or x > 2
Merging overlapping intervals:
x ≤ 1 or x > 2
Combining the intervals:
x ≤ 1 or x > 2 and x > 2
Merging overlapping intervals:
x > 2
Combining all the intervals:
x < -2 or -1 ≤ x < 0 or 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 or x >2
Merging the overlapping intervals:
x < -2 or -1 ≤ x ≤ 1 or x > 2
Therefore,
x ϵ (-∞, -2) Ս [-1,1] Ս (2, ∞)