If 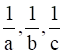 are in AP, prove that
are in AP, prove that
(i) 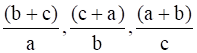 are in AP.
are in AP.
(ii) 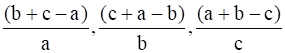 are in AP.
are in AP.
(i) ![]() are in A.P.
are in A.P.
To prove: ![]() are in A.P.
are in A.P.
Given: ![]() are in A.P.
are in A.P.
Proof: ![]() are in A.P.
are in A.P.
If each term of an A.P. is multiplied by a constant, then the resulting sequence is also an A.P.
Multiplying the A.P. with ( a + b + c )
![]() are also in A.P.
are also in A.P.
If a constant is subtracted from each term of an A.P., the resulting sequence is also an A.P.
Substracting the above A.P. with 1
![]() , are also in A.P.
, are also in A.P.
![]() , are also in A.P.
, are also in A.P.
![]() , are also in A.P.
, are also in A.P.
Hence Proved
(ii)![]() are in A.P.
are in A.P.
To prove: ![]() are in A.P.
are in A.P.
Given: ![]() are in A.P.
are in A.P.
Proof: ![]() are in A.P.
are in A.P.
If each term of an A.P. is multiplied by a constant, then the resulting sequence is also an A.P.
Multiplying the A.P. with ( a + b + c )
![]() are also in A.P.
are also in A.P.
If a constant is subtracted from each term of an A.P., the resulting sequence is also an A.P.
Substracting the above A.P. with 2
![]() , are also in A.P.
, are also in A.P.
![]() , are also in A.P.
, are also in A.P.
![]() , are also in A.P.
, are also in A.P.
Hence Proved