If 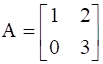 is written as B + C, where B is a symmetric matrix and C is a skew-symmetric matrix, then find B.
is written as B + C, where B is a symmetric matrix and C is a skew-symmetric matrix, then find B.
We are given that,
![]()
Where,
B = symmetric matrix
C = skew-symmetric matrix
We need to find B.
A symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose.
A symmetric matrix ⬄ A = AT
Now, let us understand what skew-symmetric matrix is.
A skew-symmetric matrix is a square matrix whose transpose equals its negative, that, it satisfies the condition
A skew symmetric matrix ⬄ AT = -A
So, let the matrix B be
![]()
Let us calculate AT.
We know that the transpose of a matrix is a new matrix whose rows are the columns of the original.
We have,
![]()
Here,
1st row of A = (1 2)
2nd row of A = (0 3)
Transpose of this matrix A, AT will be given as
1st column of AT = 1st row of A = (1 2)
2nd column of AT = 2nd row of A = (0 3)
Then,
![]()
Substituting the matrix A and AT in B,
![]()
![]()
![]()
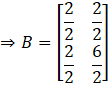
![]()
Taking transpose of B,
1st row of B = (1 1)
2nd row of B = (1 3)
Transpose of this matrix B, BT will be given as
1st column of BT = 1st row of B = (1 1)
2nd column of AT = 2nd row of A = (1 3)
Then,
![]()
Since, B = BT. Thus, B is symmetric.
Now, let the matrix C be
![]()
Substituting the matrix A and AT in C,
![]()
![]()
![]()
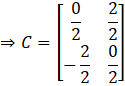
![]()
Multiplying -1 on both sides,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Taking transpose of C,
1st row of C = (0 1)
2nd row of C = (-1 0)
Transpose of this matrix C, CT will be given as
1st column of CT = 1st row of C = (0 1)
2nd column of CT = 2nd row of C = (-1 0)
Then,
![]()
Since, CT = -C. Thus, C is skew-symmetric.
Check:
![]()
Put the value of matrices B and C.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Matrices B and C satisfies the equation.
Hence, ![]() .
.