Find the value of c prescribed by Lagrange’s mean value theorem for the function ![]() defined on [2, 3].
defined on [2, 3].
![]()
f(x) will exist, if
x2 – 4 ≥ 0
x2 ≥ 4
![]() x ≤ -2 or x ≥ 2
x ≤ -2 or x ≥ 2
![]() for each x Є [2, 3], the function f(x) has a unique definite value, f(x) is continuous on (2, 3).
for each x Є [2, 3], the function f(x) has a unique definite value, f(x) is continuous on (2, 3).
![]()
![]()
Exists for all x Є (2, 3).
So, f(x) is differentiable on (2,3).
Hence, both the conditions of Lagrange’s Theorem are satisfied.
Consequently, there exists c Є (2, 3) such that,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 0
0
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Squaring both sides,
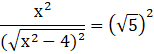
![]()
5x2 – 20 – x2 = 0
4x2 = 20
x2 = 5
x = ± √5
Hence, c = √5 Є (2, 3) such that ![]()
Hence the above explanation verifies the Lagrange’s Theorem.
1