Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
The general solution of the differential equation 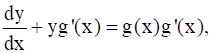 where g(x) is a given function of x, is
where g(x) is a given function of x, is
![]()
![]()
Since it is a form of linear differential equation where
P = g’(x) and Q = g(x) g’(x)
Integrating Factor (I.F) = e∫ p dx
I.F = e∫ g’(x) dx = eg(x)
Solution of differential equation is given by
y.(I.F) = ∫ Q.(I.F) dx + C
⇒ y. eg(x) = ∫ g(x). g’(x). eg(x) dx + C
Consider integral ∫ g(x). g’(x). eg(x) dx
Put g(x) = t
⇒ g’(x) dx = dt
⇒ ∫ t. et dt
Treating t as first function and et as second function, So integrating by Parts we get,
⇒ t. et - ∫ 1.et dt + C
⇒ et (t – 1) + C
Putting value of t we get,
⇒ e g(x) (g(x) – 1) + C
∴ y. e g(x) = e g(x) (g(x) – 1) + C
Dividing e g(x) both sides we get,
⇒ y = (g(x) – 1) + C e-g(x)
⇒ y - g(x) + 1 = C e-g(x)
Taking log both sides we get,
⇒ log (y – g(x) + 1) = log (C e-g(x))
⇒ log (y – g(x) + 1) = log C – g(x) log e
⇒ log (y – g(x) + 1) = log C – g(x) ∵ log e = 1
⇒ g(x) + log {1 + y – g(x)} = C ⇒ (B) where log C = C