Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
The solution of the differential equation 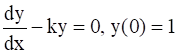 approaches to zero when x → ∞, if
approaches to zero when x → ∞, if
![]()
![]()
By variable separable and integrating both sides
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Where ec = A
Where ec = A
We have given condition y(0) = 1
![]()
![]()
![]()
We know e∞ → ∞ and e-∞ → 0
So, we are given that y approaches to zero when x → ∞
i.e. 0 = ek∞
Which is possible only when k < 0 = (C)
1