Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
If P(A) = 3/10, P(B) = 2/5 and P(A ∪B) = 3/5, then P(A/B) + P(B/A) equals
P(A) = ![]() , P(B) =
, P(B) = ![]() , P(A⋃B) =
, P(A⋃B) = ![]() → (Given)
→ (Given)
According to the addition theorem of probability for two events A and B we have,
P(A) + P(B) – P(A⋂B) = P(A⋃B)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now then,
![]()
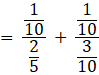
![]()
![]()
![]()
1