Match the following and choose the correct option from those given below.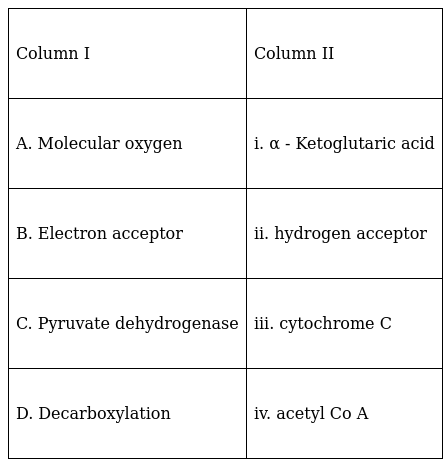
Options
A. Molecular oxygen – ii. hydrogen acceptor
The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration inaerobic organisms is oxygen because in the electron transport chain, oxygens act as the final electron acceptor and it is a highly oxidizing agent and therefore it is a powerful electron acceptor.
B. Electron acceptor – iii. Cytochrome C
The cytochrome C is a protein enzyme which is located between the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane. It is responsible for the transfer of electron and it is the major electron acceptor.
C. Pyruvate dehydrogenase – iv. acetyl CoA
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) is a complex of enzymes that converts the pyruvate into the acetyl-CoA by a process known as pyruvate decarboxylation.
D. Decarboxylation – i. α - Ketoglutaric acid
α - Ketoglutaric acid is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle i.e., tricarboxylic cycle (TCA cycle). The decarboxylation oxalosuccinate forms the alpha - ketoglutaric acid in a decarboxylation reaction of the TCA cycle.