An air bubble of radius 2.0 mm is formed at the bottom of a 3.3 m deep river. Calculate the radius of the bubble as it comes to the surface. Atmospheric pressure = 1.0 × 105 Pa and density of water = 1000 kg m–3.
Given
Radius of bubble at the bottom of deep river R1=2.0mm=2.0![]() m
m
Depth of the river h=3.3m
Density of water ![]() = 1000 kg m–3
= 1000 kg m–3
We know that
Pressure at depth inside a fluid is related to atmospheric pressure by relation
P1=Pa + h![]() g
g
Where P1 =pressure at depth h
Pa=atmospheric pressure=1.0 × 105 Pa
g=acceleration due to gravity=9.8ms-2
![]() =density of fluid.
=density of fluid.
So,
P1=1.0![]() 105+3.3
105+3.3![]() 1000
1000![]() 9.8=1.32
9.8=1.32![]() 105Pa
105Pa
Temperature is same for both water at the bottom and the water at the surface. So, we can apply Boyle’s law which says that PV=constant, when temperature is constant.
Let V1 be the volume of air bubble at bottom of deep river
![]()
Va be the volume of air bubble at surface of river
![]()
Where Ra = radius of bubble at surface of river
So, according to Boyle’s law
P1 V1=Pa Va
![]()
![]()
![]()
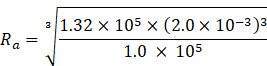
Ra=2.2![]() 10-3m
10-3m
![]() Radius of the air bubble at the surface of river is 2.2
Radius of the air bubble at the surface of river is 2.2![]() 10-3m.
10-3m.