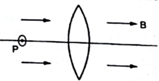
Figure shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic field B of magnitude 1.2 T parallel to tis principal axis. A particle having a charge 2.0 × 10–3 C and mass 2.0 × 10–6 kg is projected perpendicular to the plane of the diagram with a speed of 4.8 ms–1. The particle moves along a circle with its centre on the principal axis at a distance of 18 cm from the lens. Show that the image of the particle goes along a circle and find the radius of that circle.
Given-
Focal length of the convex lens = 12 cm
Uniform magnetic field, B = 1.2 T
Charge of the particle, q = 2.0 × 10−3 C
an mass, m = 2.0 × 10−5 kg
Speed of the particle, v = 4.8 m s−1
Distance between the particle and the lens = 18 cm
Given in the question that the object is projected perpendicularly on the plane of the paper.
The radius of the circular path described by a particle in a magnetic field r,
![]()
where,
m is the mass of a proton
v= velocity of the particle
B = magnetic force
q= charge on the particle =![]() C
C
![]()
![]()
![]()
Given that, the object distance, u = -18 cm
Using the lens formula –
![]()
where,
v=distance of image formed from lens
u=distance of the object from lens
f =focal length of the lens
substituting the values-
![]()
![]()
Let the radius of the circular path of image be r’.
Hence magnification -
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore, the radius of the circular path in which the image of the object formed from the lens moves is 8 cm.