A gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCA as shown in the figure. If 2.4 cal of heat is given in the process, what is the value of J?
‘J’ is mechanical equivalent of heat a conversion factor between two different units of energy: calorie to joule
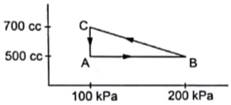
From the graph we can write
VA=VB=500cc=500×10-6m3
VC=700cc=700×10-6m3
PA=PC=100kPa=100×103 Pa
PB=200kPa=200×103Pa
We know that work done by the gas is given as
ΔW=PΔV
Work done in path AB=0 as VA=VB.
Work done in path CA ΔW1=PA(VA-VC)
=100×103× (500-700)×10-6
=-20J
Work done in path BC ΔW2= Pavg(VC-VB)
![]()
ΔW2=150×103×(700-500)×10-6
=30J
Total work done in process ABCA=ΔW=ΔW1+ΔW2
=30-20=10J
We know that in the cyclic process the system returns to its initial state. So, change internal energy in the cyclic process will be zero as internal energy is a state function.
From first law of thermodynamics, we know that,
ΔQ=ΔU+ΔW
Where ΔQ=heat supplied to the system
ΔU=change in internal energy
ΔW=work done by the system
Since ΔU=0, first law becomes
ΔQ=ΔW=10J
But it is given in question that ΔQ=2.4cal
So, 2.4×J=10Joule
![]()
∴ value of ‘J’ is 4.17J/cal.