A small plane area is rotated in an electric field. In which orientation of the area is the flux of the electric field through the area maximum? In which orientation is it zero?
The flux of electric field through an area is defined as the number of field lines that pass through that area in the direction of the electric field.
In mathematical terms,
Flux![]()
Where,
E = electric field vector,
ds = small area element.
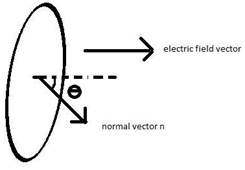
Now, ds = nda, where n is the unit normal in the direction of the area, and da is a small area element.
By the law of dot product in vector calculus,
E.ds = |E||ds|cos θ,
Where θ is the angle between the normal to the area and the electric field.
|E| = magnitude of electric field vector,
|ds| = magnitude of small area element.
Now, the flux is maximum when cos θ = 0 or 180°, since cos 0 or cos 180° = +1 or –1.
In this case, the flux will be |E||ds|. In all other cases, the flux will be less than this.
The flux is minimum when cos 90°, since cos 90° = 0.
Φ=|E||ds| cos(90o) =0
Thus, when the unit normal vector perpendicular to the direction of the electric field the flux is ZERO.