A closed surface S is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface S is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface.
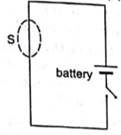
At any interval of time, the net charge enclosed by the surface S is zero, since an equal number of electrons enter and leave the surface. So the charge enclosed is 0.
According to Gauss’ law, electric flux through a closed surface is equal to 1/ϵ0 times the charge enclosed by the surface.
![]() ,
,
Where
1