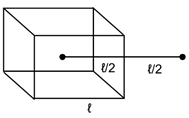
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a rod of length ℓ. Consider a hypothetical cube of edge ℓ with the centre of he cub at one end of the rod. Find the minimum possible flux of the electric field through the entire surface of the cube.
Given:
Length of rode=edge of cube=l
Portion of rod inside cube=l/2
Total charge =Q
Linear charge density of rod = Q/l of rod=λ
By Gauss’s law, flux of net electric field through a closed surface equals the net charge enclosed by the surface divided by ϵ0
![]() …..(i)
…..(i)
Where qin is the net charge enclosed by the surface through which the flux is calculated.
E⃗ =net electric field at the surface
dS⃗ =area of differential surface element
Using gauss law flux through the cube is given by Qin/ϵ0 where
Qin is the charge enclosed by the cube
Charge enclosed by the cube is given by charge density × length of rod inside cube
![]()
⇒ ![]()
∴ by (i)
Flux![]()
Therefore flux of electric field through the entire surface of cube is given by Q/2ϵ0