A charged particle having a charge of –2.0 × 10–6 C is placed close to a nonconducting plate having a surface charge density 4.0 × 10–6 C m–2. Find the force of attraction between the particle and the plate.
Given:
Charge of the particle= -2.0× 10-6C=q
Surface charge density=4.0× 10-6C/m2 =σ
The electric field due to a plane thin sheet of charge density σ is given by
![]()
Proof:
To calculate the electric field at P we choose a cylindrical Gaussian surface as shown in the fig. in which the cross section A and A’ are at equal distance from the plane.
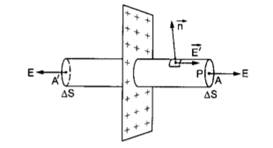
The electric field at all points of A have equal magnitude E. and direction along positive normal. The flux of electric field through A is given by
![]()
Since A and A’ are at equal distance from sheet the electric field at any point of A’ is also equal to E and flux of electric field through A’ is also given by
E.ΔS
At the points on curved surface the field and area make an angle of 90° with each other and hence ![]()
The total flux through the closed surface is given by
![]() ..,(i)
..,(i)
The area of sheet enclosed in the cylinder is given by ΔS
So the charge contained in the cylinder is given by
![]() …(ii)
…(ii)
We know that,
By Gauss’s law, flux of net electric field (E⃗ ) through a closed surface S equals the net charge enclosed by the surface (qin) divided by ϵ0
![]()
Using gauss law and eqns(i) and (ii)
![]()
![]() ..(iii)
..(iii)
Now,
Force F⃗ on a charge particle of charge q in presence of electric field E⃗ is given by
![]()
Using eqn(iii),we get
![]()
Putting the values of σ and q we get
![]() N
N
![]() N(-ve sign indicates that the force is attractive in nature)
N(-ve sign indicates that the force is attractive in nature)
Therefore force of attraction between the particle and the plate is given by 0.45N