One end of a steel rod (K = 46 J s–1 m–1 °C–1) of length 1.0 m is kept in ice at 0°C and the other end is kept in boiling water at 100°C. The area of cross-section of the rod is 0.04 cm2. Assuming no heat loss to the atmosphere, find the mass of the ice melting per second. Latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 × 105 J kg–1.
Given:
Thermal conductivity of the steel rod : K=46 J s–1 m–1 °C–1.
Length of the rod : x = 1 m
As heat flows from area of high temperature to low temperature,
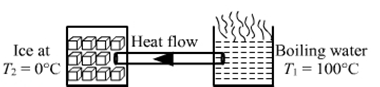
Temperature of the end in water : T1 = 100° C
Temperature of the end in ice : T2 = 0° C
Area of cross section of the rod :
A = 0.04 cm2 = 0.04× 10-4 m2.
Latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 × 105 J kg–1.
Formula used:
Rate of amount of heat flowing is given as:![]()
Here, Δθ is the amount of heat transferred, ΔT is the temperature difference, K is the thermal conductivity of the material, A is the area of cross section of the material and x is the thickness of the material.
Also,
Δθ = Q =L× m
Here, Q is the amount of heat absorbed or released, L is the Latent heat and m is the mass of the substance.
Here, Δt = 1 second.
Substituting,![]()
![]()
![]()
∴ m = 5.47 × 10-8 kg
Hence, mass of the ice melting per second is 5.47 × 10-8 kg.