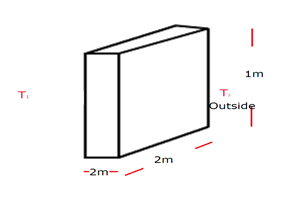
A room has a window fitted with a single 1.0 m × 2.0 m glass of thickness 2 mm.
(a) Calculate the rate of heat flow through the closed window when the temperature inside the room is 32°C and that outside is 10°C.
(b) The glass is now replaced by two glass panes, each having a thickness of 1 mm and separated by a distance of 1 mm.
Calculate the rate of heat flow under the same conditions of temperature. Thermal conductivity of window glass = 1.0 J s–1m–1 °C–1and that of air = 0.025 J s–1m–1 °C–1.
The diagram is shown –
(a) Given
Thickness, l = 2 mm = 0.0002 m
Temperature inside the room = 32°C
outside = 10°C
Dimensions of wall = 1.0 m × 2.0 m
Rate of flow of heat
= ![]()
Where,
∆T = is change in temperature between the two sides of the window.
A= Area of cross section of the window
K = thermal conductivity of the window
L = length of the window
=![]()
= 8000J/s
(b). Resistance of glass-
The equivalent circuit for the two glass panes and air becomes
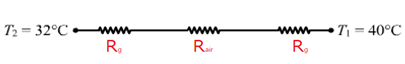
Here resistance of glass Rg = ![]()
And of air Rair = ![]()
Since, these are connected in series, equivalent resistance becomes
Reqv = ![]()
Thermal conductivity of window glass ![]() = 1.0 J s–1m–1 °C–1
= 1.0 J s–1m–1 °C–1
And of air,![]() = 0.025 J s–1m–1 °C–1.
= 0.025 J s–1m–1 °C–1.
Substituting values
Reqv =![]() (
(![]() +
+ ![]() )
)
= ![]() (
( ![]() +
+ ![]() )
)
= 0.021
Now, rate of heat flow
![]()
= ![]()
= 380.95