The dielectric constant decreases if the temperature is increased. Explain this in terms of polarization of the material.
When a polar or non polar material is placed in an external electric field , the electron charge distribution inside the material is slightly shifted opposite to the electric field and this induces a dipole moment in any volume of the material.
The polarization vector P⃗ is defined as this dipole moment per unit volume.
When a dielectric rectangular slab is placed in an external electric field the dipoles get aligned along the field and the right and left surfaces of slab gets positive and negative charges as shown in fig. known as induced charge.
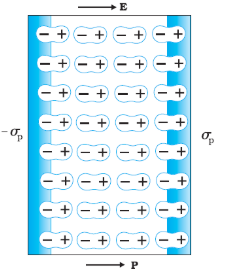
The more the dipoles are aligned with the external field , the more the dipole moment and thus more is the polarization.
Because of these induced charges an extra electric field is produced inside the material opposite to the direction of external field and the net electric field is given by
![]()
Where ,
K is the constant for a given dielectric known as dielectric constant of the dielectric >1)
E0 is the field in vacuum.
On increasing temperature, the random motion of molecules or dipoles increases due to thermal agitation and the dipoles get less aligned with the electric field and thus dipole moment decreases.
Since polarization is given by dipole moment per unit volume, it also decreases
And since ,dielectric constant is described by the polarization of the material
Thus, on increasing temperature, dielectric constant decreases.