A 5.0 μF capacitor is charged to 12V. The positive plate of this capacitor is now connected to the negative terminal of a 12V battery and vice versa. Calculate the heat developed in the connecting wires
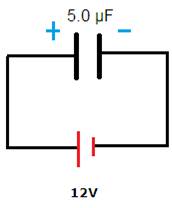
Given
Initially 5.0 μF capacitor is charged to 12V as shown in fig.
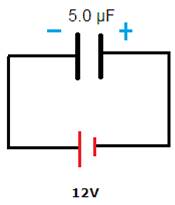
Next, the positive plate of this capacitor is now connected to the negative terminal of a 12V battery as shown in fig.
When the capacitor is connected to the battery of 12V with first plate to positive and second plate to negative, a positive charge Q = CV appears on one plate where, C is the capacitance and v is the voltage applied, and –Q charge appears on the other.
When the polarity is reversed, a charge –Q appears on the first plate and +Q on the second plate.
A total charge of 2Q accumulates on the negative plate.
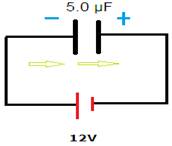
Therefore, 2Q charge passes through the battery from the negative to the positive terminal.
The battery does a work-
![]()
Where,
Q = charge and v= applied voltage
Since, a total charge of 2Q accumulates on the negative plate
⇒ ![]()
We know, Q = C×v
Where c= capacitance and v= applied voltage
![]()
The energy stored in the capacitor is the same in the two cases
and the work done by battery dissipates as heat in the connecting wires.
Hence, the heat produced is -
![]()
Given , C = 5.0 μF and voltage v = 12V
⇒ ![]()
![]()
![]()