Figure shows two parallel plate capacitors with fixed plates and connected to two batteries. The separation between the plates is the same for the two capacitors. The plates are rectangular in shape with width b and lengths ℓ1 and ℓ2. The left half of the dielectric slab has a dielectric constant K1 and the right half K2. Neglecting any friction, find the ratio of the emf of the left battery to that of the right battery for which the dielectric slab may remain in equilibrium.
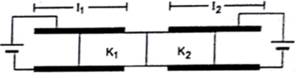
Let V1, V2 be the potential of the battery connected to the left capacitor and that of the battery connected to the right capacitor
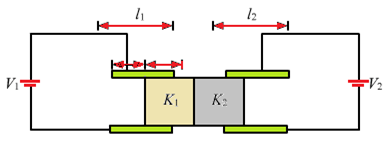
Considering the left capacitor -
Let the length of the part of the slab inside the capacitor be x.
The left capacitor can be considered to be two capacitors in parallel.
Let the battery connected to the capacitor be of potential V.
Let the length of the part of the slab inside the capacitor be x.
b – Width of plates
The capacitances of the two capacitors in parallel is given by –
![]()
![]()
C1 is the part of the capacitor having the dielectric inserted in it and C2 is the capacitance of the part of the capacitor without dielectric.
As, C1 and C2 are in parallel therefore, the net capacitance is given by![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore, the potential energy stored in the left capacitor will be
![]()
![]() 1)
1)
This dielectric slab is attracted by the electric field of the capacitor and applies a force.
Let assume that electric force of magnitude F pulls the slab toward left direction.
Let there be an differential displacement dx towards the left direction by the force F.
The work done by the force
![]()
Let V1 and V2 be the potential of the battery connected to the left capacitor and that of the battery connected with the right capacitor
With increase in the displacement of slab, the capacitance will increase, hence the energy stored in the capacitor will also increase.
Let us consider a small displacement dx of the slab towards the inward direction.
In order to maintain constant voltage, the battery will supply extra charge, and gets damage .
Therefore the battery will do work.
Now,
Work done by the battery
= Energy change of capacitor + work done by the force F on the capacitor
![]() 1)
1)
Let’s take the differential charge dq is supplied by the battery, and the change in the capacitor be dC
We know that energy in capacitor dWB
![]()
we know q = cv
⇒![]() 2)
2)
And force F is given by,
![]()
![]()
From 1) and 2)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solving for voltages V1 and V2 -
![]()
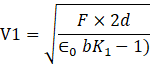
Similarly, for the right side the voltage of the battery is given by-
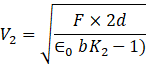
Now, the ratio of the voltages is given by-
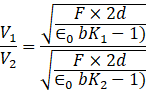
![]()
Thus, the ratio of the emfs of the left battery to the right battery is given by -
![]()