Name the two nucleic acids present in a cell. What are their functions?
Everything in the world is made up of elements, but nucleic acids are made up of only 5 elements. These are Oxygen (O), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N), Carbon (C) and Phosphorus (P). These elements combine into specific orientations and give rise to genetic material of living organisms. These two nucleic acids are:
i. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): This double helix structure encodes the basic instructions of living organisms. This is the reason why children have characteristics similar to their parents, as this nucleic acid passed down from generation after generation with multiple modifications thus distinguishing you a bit from your parents. It recites inside the nucleus of a cell. This twisted staircase structure is made up of four nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). It is composed of deoxyrisbose sugar. It was discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick. This genetic material is enclosed in a nuclear envelope of only eukaryotes and the two membranes bound organelles called mitochondria and chloroplast. They are not protected by a nuclear envelope in prokaryotic organisms.
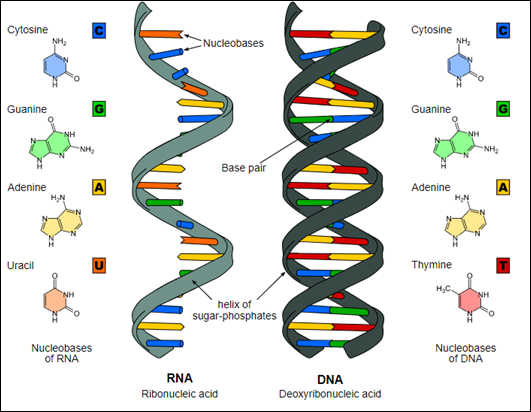
ii. RNA (ribonucleic acid): It is the genetic material of viruses. This RNA has major role in protein synthesis inside a cell. Their structure is also made up of four nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and Uracil (U). Here thymine is replaced by uracil. Another difference between RNA and DNA is that RNA is single stranded. It was discovered by Friedrich Miescher. It is composed of ribose sugar. RNA is of three types:
• rRNA (ribosomal RNA) which do protein synthesis.
• mRNA (messenger RNA) which transfer code from DNA to the nucleus for rRNA to do its work.
• And, tRNA (transfer RNA) carries various amino acids to ribosomes.