Name the three major functional regions of cells. Briefly mention the components of each and explain the function of each.
Cells are the smallest entity within a living cell. It is the structural and functional part of all living organisms. So we can say all living like dog, cat, human, horse, insects have multiple cells having multiple specific functions.
So there are two types of cells, unicellular and multi-cellular. And then further its animal cell and plant cell, but all the types of cell have three major functional regions:
(a) Cell Membrane
(b) Nucleus
(c) Cytoplasm
Cell Membrane
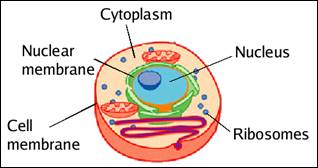
Every cell has an outer layer which regulates the inflow and outflow of various substances from a cell which is called a cell membrane. It is also called a plasma membrane. Its main function is to surround and protect the cytoplasm of the cell. Everything from outside has to cross the barrier which is cell membrane only then they can go inside of a cell. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions like hydrogen, calcium, sodium, small molecules like oxygen (O2), Carbon-dioxide (CO2) and various larger molecules such as amino acids, glucose, sucrose, etc. Cell membrane performs various functions inside a cell which are osmosis, diffusion, transport of nutrients and molecules into the cell, waste removal, etc. The membrane is made of phospholipids bilayer having protein and carbohydrate molecules infused within the lipid bilayer. This fluid-structure provides enough mechanical support and flexibility to allow cells to grow and move.
The Fluid Mosaic Model of the cell membrane was proposed and explained by S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson in 1972. The specific proteins present in the double layered membrane are very important for cell-cell recognition and interaction. This interaction allows various cells to acquire oxygen, nutrients, water etc. So basically the cell membrane acts as a gate which keeps the thing outside and inside when it wants.
Cytoplasm
It is the jelly-like component within the cell which holds everything in its place. It is mostly composed of water along with various nutrients and waste products required by the cell. It provided the enriching environment within the cell for several metabolic reactions to occur systematically.
It serves various functions within the cell:
• It provides mechanical strength to the cell by exerting turgor pressure against the cell's membrane thus maintaining the shape of the cell.
• It is the place for the functioning of most regulatory activities like metabolism, cell division, and protein synthesis within the cell.
• The cytoplasm contains organelles called ribosomes which do protein synthesis.
• It is referred to as the storage house for various small carbohydrate, lipid and protein molecules.
• The cytoplasm can transport and distribute organelles in a discrete manner around the cell.
Nucleus
The nucleus is also called as brain of the cell. It contains the code of life within itself, i.e. DNA (Deoxy-ribonucleic acid) which codes the genetic information of a living entity. It is the largest organelle within the cell. It is present in the eukaryotic cell but is absent in prokaryotic cell, because of which they can be highly distinguished. It has its own covering which separates it from its surrounding cytoplasm called the nuclear envelope. Also, the envelope has certain small pores which regulate the exchange of materials like protein, RNA, etc between the cytoplasm and nucleus. It has chromatin material within the cell consisting of thin long threads of DNA encircled around protein.
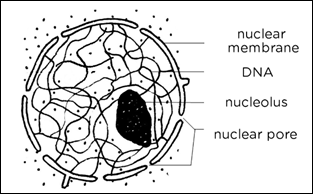
Nucleus performs various functions like:
• It controls gene expression and facilitates the replication of DNA during the cell.
• It controls the metabolic reactions within the cell by producing mRNA which codes for enzymes.
• It is the site for protein synthesis, for example, it synthesizes structural proteins like actin which helps in maintaining the shape of the cell.
• It is also the site for ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis, which secretes ribosomes which are important for translation of proteins.
• It is responsible for the transfer of Character from parent to offspring via genetic material (DNA) present inside the nucleus.