Match the defects given in Column I with the statements in given Column II.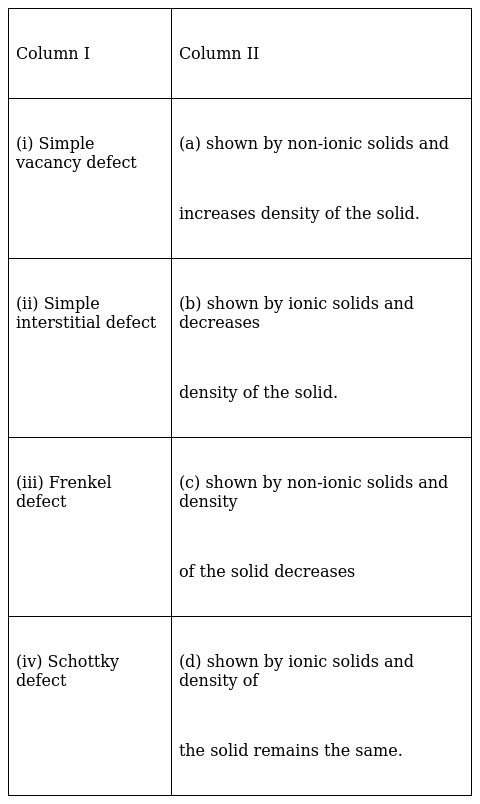
(i)-c , (ii)-a , (iii)-d , (iv)-b
(i) Simple vacancy defect: when some lattice sites are absent from the crystal creating voids, it is called vacancy defect. Since some ions or atoms leaves the site it results in decrease in density.
(ii) Simple Interstitial defect: when some atoms or molecules leaves their sites and move to interstitial sites, it is called Interstitial defect. Since there is no net movement of atoms from the crystal, density remains same.
(iii) Frenkel defect: In this type of defect, the smaller ion (normally cation) moves to interstitial sites leaving vacancy space in its original site. Thus, like simple interstitial defect density remains same. This defect is shown by ionic solids like ZnS, AgCl, AgBr etc.
(iv) Schottky Defect: Unlike interstitial defect, it is vacancy defect in which both cations and anions leaves their crystal lattice. To maintain electrical neutrality both leaves in same number. Like simple vacancy defect, density decreases in this type of defect. Ex. NaCl, KCl, AgBr etc..