Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C4H9Br is treated with aq. KOH solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another optically active isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. KOH solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and KOH both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration?
The compound ‘A’, C4H9Br when treated with aq. KOH, proceeds with the rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of ‘A’ only. This means that the reaction follows first order kinetics, which is the characteristic of SN1 reactions. This means C4H9Br is a tertiary halide, because tert-halides undergo SN1 reactions. On the other hand, the optically active isomer ‘B’, when subjected to treatment with aq. KOH, undergoes SN2 reaction due to the rate of reaction depending on both the reactants. This means that the isomer is a secondary halide.
(i) The structure of ‘A’ is
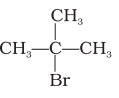
The structure of ‘B’ is 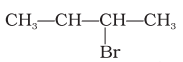 .
.
(ii) Compound ‘B’ will undergo inversion of configuration and give inverted product because it undergoes SN2 reaction.