Elimination reactions (especially b-elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. Specify the reagents used in both cases.
Alkyl halides can undergo both beta-elimination as well as substitution reactions, the desired product can be obtained using an appropriate reagent and environmental conditions of the system. Consider the case of CH3CH2Br, which can undergo β-elimination as well as substitution. On treatment with alcoholic KOH, at 473-523°K, ethyl bromide undergoes elimination to give ethane. On the other hand, treatment with aqueous KOH at a lower temperature of 373°K gives ethyl alcohol by substitution reaction.
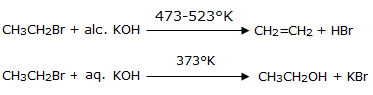
2