Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.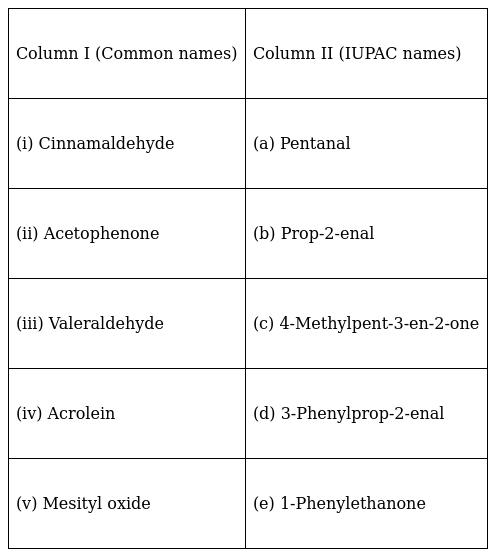
(i) Cinnamaldehyde - (d) 3-Phenylprop-2-enal
(ii) Acetophenone - (e) 1-Phenylethanone
(iii) Valeraldehyde - (a) Pentanal
(iv) Acrolein - (b) Prop-2-enal
(v) Mesityl oxide - (c) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
EXPLAINATION:
i) The structure of Cinnamaldehyde is:
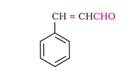
Here, a phenyl group is attached to a carbon atom at 3rd position with respect to the functional group. A double bond is present between the C2 and C3 atoms. Thus, the IUPAC name of Cinnamaldehyde is 3-Phenylprop-2-enal.
ii) The structure of Acetophenone is:
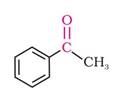
Here, the functional group present in the above structure is ketone. This ketone group is attached to one methyl group and one phenyl ring.
Thus, the IUPAC name of Acetophenone is 1-Phenylethanone.
iii) The structure of Valeraldehyde is:
CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO
The functional group in this compound is aldehyde. The number of carbon atoms in the longest chain is five. Thus, the IUPAC name of Valeraldehyde is Pentanal.
iv) The structure of Acrolein is:
CH2=CH-CHO
The functional group in this compound is aldehyde. The number of carbon atoms in the longest chain is three with one double bond between C2 and C3 atoms. Thus, the IUPAC name of Acrolein is Prop-2-enal.
v) The structure of Mesityl oxide is:
(CH3)2C=CHCOCH3
The functional group in this compound is ketone. The number of carbon atoms in the longest chain is five with one double bond between C3 and C4 atoms. Thus, the IUPAC name of Mesityl oxide is 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one.