Match the reactions given in Column I with the statements given in Column II.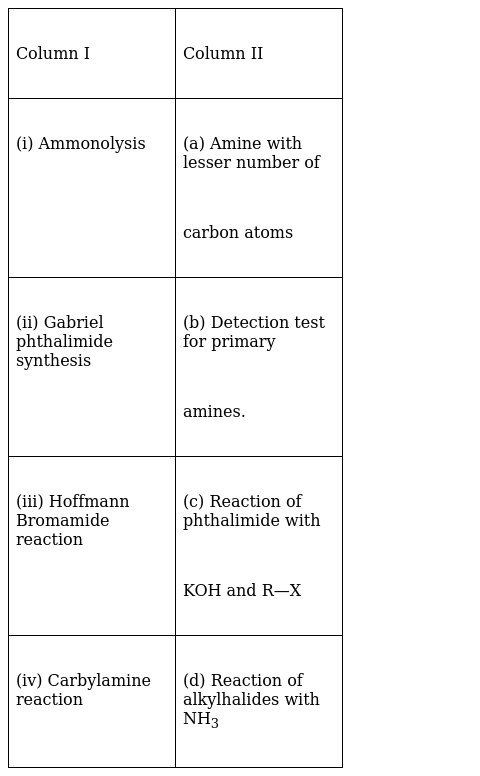
(i) Ammonolysis - (d) Reaction of alkylhalides with NH3
(ii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis - (c) Reaction of phthalimide with KOH and R—X
(iii) Hoffmann Bromamide reaction - (a) Amine with lesser number of carbon atoms
(iv) Carbylamine reaction - (b) Detection test for primary amines.
(i) Ammonolysis - (d) Reaction of alkylhalides with NH3
Alkylhalides are treated with NH3 to form amines. The C-halogen bond is cleaved by NH3 molecules.
(ii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis - (c) Reaction of phthalimide with KOH and R—X
Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of primary amines. Phthalimide is treated with KOH to form potassium salt of phthalimide which on heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis produces the corresponding primary amine.

(iii) Hoffmann Bromamide reaction - (a) Amine with lesser number of carbon atoms
Hoffmann Bromamide reaction is used for the preparation of primary amines by treating an amide with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide.

(iv) Carbylamine reaction - (b) Detection test for primary amines.
Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines on heating with chloroform and KOH form isocyanides or carbylamines which are foul smelling substances but secondary and tertiary amines do not show this reaction. Thus, Carbylamine reaction can be used to detect primary amines.
![]()