Predict the reagent or the product in the following reaction sequence.
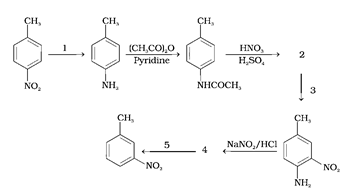
When p-Nitrotoluene undergoes reduction, it forms p-methyl benzyl amine. The reagents for ‘1’ are Sn + HCl or Fe + HCl which cause the reduction due to release of hydrogen. Even hydrogen gas passed over finely divided nickel, platinum or palladium in the presence of steam works to drive the reaction.
N-Methylaniline undergoes acetylation in the presence of a strong base such as pyridine to form N-methylacetanilide. The next step is nitration, with the reagents given which are HNO3 and H2SO4. Due the presence of the acetyl group, nitration leads to the formation of 2-Nitro-4-methylacetanilide. Hence, ‘2’ is 2-Nitro-4-methylacetanilide.
This molecule undergoes a reaction with reagent ‘3’ to give 2-nitro-4-methylaniline. This means ‘2’ undergoes hydrolysis to give 2-nitro-4-methylaniline. ‘3’ is H2O/H+.
2-nitro-4-methylaniline further reacts with NaNO2/HCl which forms a diazonium salt, hence ‘4’ is a diazonium salt 2-nitro-4-diazonium chloride.
After reaction with reagent ‘5’, the product formed does not have the N2+Cl- group at 4C. This means the diazonium chloride has been displaced by H. Hence the reagent ‘5’ is a mild reducing agent like hypophosphorous acid H3PO2 (phosphinic acid) or ethanol. The reagents themselves get oxidised to phosphorous acid and ethanal, respectively.
