An amount Q of heat is added to a monatomic ideal gas in a process in which the gas performs a work Q/2 on its surrounding. Find the molar heat capacity for the process.
Given: Amount of heat added(dQ) = Q
Amount of work done(dW) = Q/2.
Formula used:
dQ(heat) = dU(internal energy) + dW(work done).
Here, heat = Q and Work = Q/2(given)
=> ![]() .
.
We can write U = nCvdT and Q = nCdT, where n = no of moles, Cv = specific heat capacity at constant volume(when dQ = dU), C = molar heat capacity and dT = change in temperature.
Therefore, 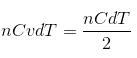 => C = 2Cv.
=> C = 2Cv.
For a monoatomic ideal gas, we know that Cv = (3R/2) J/kg/mol,
Where R = universal gas constant = 8.314 J/kg/mol
Therefore, C = 2*(3R/2) = 3R J/kg/mol. (Ans)
1