Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
A (g) + 2 B (g) → 2C (g)
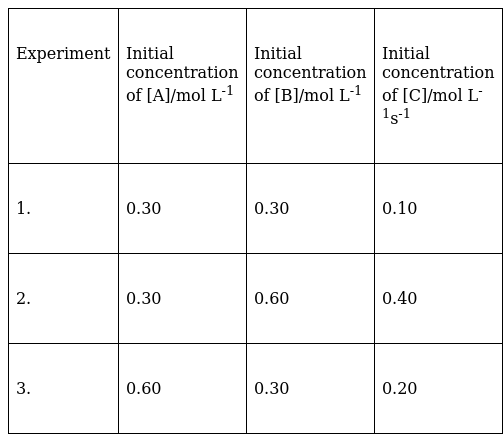
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
We know that the
Rate=k[A]x[B]y
To determine the value of x and y, We will use the data given in the table
By observing that when the concentration of B is doubled keeping the molar concentration of A constant the rate of production of C changes from .10 to .40, it means then the rate of production of C or Rate is directly proportional to the square of the molar concentration of B.
By keeping the concentration of B constant and on doubling the concentration of A from .30 to .60, the rate of production of C changes from .1 to .2, this means that the rate of production of C or Rate is directly proportional to the molar concentration of A.
Hence, x=1 and y=2,
Rate=k[A][B]2
The value of x and y, for the other options, do not give the correct value rate of production of C for the respective value of A and B.