Match the class of compounds given in Column I with their functions given in Column II .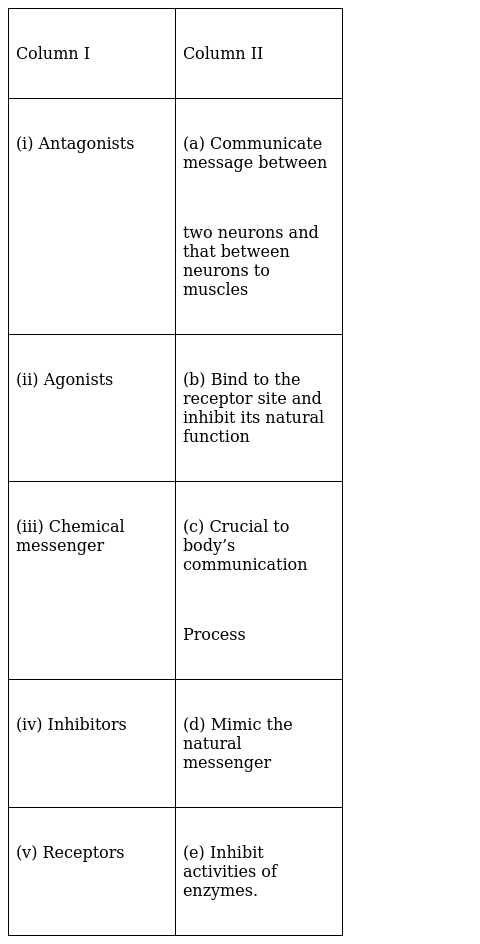
(i) Antagonists – (b) Binds to the receptor site and inhibit its natural function
Antagonists in biochemistry, is a type of receptor ligand which binds and blocks a receptor by which the biologic response is dampened. Instead of activating, its function is inhibitory. For example dopamine antagonist is a drug which blocks the dopamine receptors.
(ii) Agonist – (d) Mimic the natural messenger
The functioning nature of an agonist is complementary to that of an antagonist.
Agonists are chemical which binds to a receptor and activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Thus its action is activating.
When they switch on the receptors, agonists mimic the natural messenger. So, they are used when there is lack of natural chemical messenger.
(iii) Chemical messenger – (a) Communicate message between
two neurons and that between neurons to muscles
As we know, from the name itself that a messenger should be something which is used in communication. Similarly, chemical messenger should be something which communicate ‘chemical messages’, which are electrical impulses, between two neurons and also between neurons to muscles.
(iv) Inhibitor – (e) Inhibit activities of enzyme
From the name we can identify inhibitors have some inhibiting nature. So what does it inhibit?
Inhibitors block the binding site of an enzyme and prevent the substrate from binding to it as a result, the catalytic activity of that enzyme is inhibited.
(v) Receptors – (c) Crucial to body’s communication process
Receptor is a crucial part to our body’s communication process. They are structures found in cell membrane and are made of proteins called glycoproteins. Receptors bind to specific molecules.
If the receptor has that molecule, we say that the molecule is activated else it is deactivated.