A natural linear polymer of 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene becomes hard on treatment with sulphur between 373 to 415 K and —S—S— bonds are formed between chains. Write the structure of the product of this treatment?
The structure of 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene is the following:
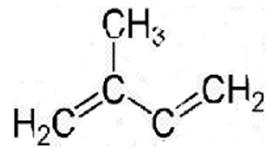
A linear polymer of 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene is known as natural rubber. It is brittle at low temperature below 283K. But when this raw rubber is heated between 373K to 415K with sulphur in presence of a suitable additive, sulphur forms a cross-linking. The double bonds act as reactive sites where this cross-linking occur. During this reaction, the double bonds are broken and new S-S bonds are formed.
This process is known as vulcanization of rubber. Sulphur here acts as a crosslinking agent and the rubber gets stiffened during this process having improved physical properties than natural rubber.