The current voltage characteristic of an ideal p-n junction diode is given by
i = i0 (eeV/kT – 1)
Where the drift current i0 equals 10 μA. Take the temperature T to be 300 K.
(a) Find the voltage V0 for which eeV/kT = 100. One can neglect the term 1 for voltages greater than this value.
(b) Find an expression for the dynamic resistance of the diode as a function of V for V > V0.
(c) Find the voltage for which the dynamic resistance is 0.2 Ω
The current voltage characteristic of ideal p-n junction diode is
![]()
(a) For large value of voltages, 1 can be neglected. So, the relation becomes
![]()
We need to find the value of V0 for which eev/kT=100
It is given that T=300K, i0=10μA and i=100
Taking natural log to both sides,
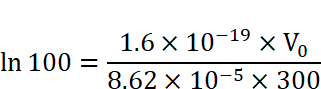
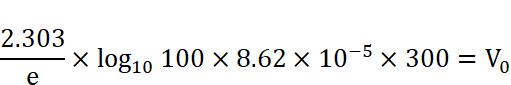
V0=0.12V
(b) Dynamic Resistance of the diode, R= Rate of change of voltage with respect to current
• ![]()
We know, 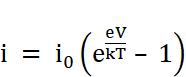
Differentiating both sides with respect to V,
• ![]()
• ![]()
• ![]()
(c) Given, R = 0.2Ω
• ![]()
• ![]()
• ![]()
• ![]()
k=8.62×10-5
T=300K
i0=10μA
R=0.2Ω
e=1.6×10-19 C
On substituting the values, we will get V=0.25 V