A copper wire bent in the shape of a semicircle of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the emf induced between the ends of the wire if
(a) the velocity is perpendicular to the diameter joining free ends,
(b) the velocity is parallel to this diameter.
Given:
Radius of semicircular wire=r
Velocity =v
We know that,
motional emf produced due to a conductor of length l moving with velocity v in a magnetic field B is given by
![]()
In the case of semicircular wire, l denotes the effective length of wire perpendicular to velocity.
(a) when the velocity is perpendicular to diameter joining free ends
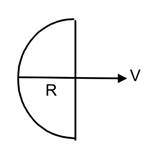
the effective length of wire perpendicular to velocity is given by length of diameter
∴ ![]()
Therefore, induced emf in the wire is given by
![]()
Therefore, induced emf in this case is 2BvR
(b) when the velocity is parallel to the diameter
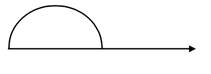
The effective length of wire parallel to velocity is zero
∴ ![]()
Therefore, induced emf in the wire is given by
![]()
Therefore, induced emf in this case is zero