Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation ℓ. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
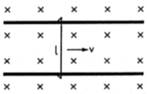
Given:
Velocity of wire=v
Separation between rail=l
We know that,
Force experienced by a wire of length l carrying current I in a magnetic field B and placed perpendicular to magnetic field is given by
![]()
Now since here there is no formation of closed circuit the circuit is open and the current flowing in the wire =0
Therefore, force experienced by wire due to magnetic field =0
Hence net force on wire becomes zero and it moves with constant velocity v
Therefore, no external force is needed to move the wire with velocity v