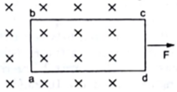
A rectangular frame of wire abcd has dimensions 30 cm × 80 cm and a total resistance of 2.0 Ω. It is pulled out of a magnetic field B = 0.020 T by applying a force of 3.2 × 10–6 N (figure). It is found that the frame moves with constant speed. Find
(a) this constant speed,
(b) the emf induced in the loop,
(c) the potential difference between the points a and b and (d) the potential difference between the points c and d.
Given:
Length ab = cd = 30 cm = 0.3 m
Length bc = ad = 80 cm = 0.8 m
Total resistance R = 2 Ω
Magnetic field B = 0.02 T
Force F = 3.2 × 10–6 N
Formula used:
(a) Magnetic force on a current carrying wire ![]() … (i),where I = current, l = length of wire, B = magnetic field.
… (i),where I = current, l = length of wire, B = magnetic field.
Hence, current ![]() … (ii)
… (ii)
Now, emf ![]() … (iii), where B = magnetic field, l = length of wire, v = constant velocity with which it is moving
… (iii), where B = magnetic field, l = length of wire, v = constant velocity with which it is moving
Also, by Ohm’s law, ![]() … (iv), where I = current,
… (iv), where I = current,
R = resistance.
Hence, equating (iii) and (iv) and substituting I from (ii), we get
![]() , where B = magnetic field, v = velocity, F = force, R = resistance, l = length of wire.
, where B = magnetic field, v = velocity, F = force, R = resistance, l = length of wire.
Here, since the force is applied on the side cd, we consider
l =30 cm = 0.3 m (the shorter length).
Hence,
Substituting the given values, we get
![]() ms-1 = 0.18 ms-1
ms-1 = 0.18 ms-1
Constant speed with which the frame moves = 0.18 ms-1(Ans)
(b) Emf induced in the loop ![]() , where B = magnetic field, l = length of the wire which is moving, v = velocity
, where B = magnetic field, l = length of the wire which is moving, v = velocity
Hence, ![]() = 0.001 V
= 0.001 V
Emf induced in loop = 0.001 V (Ans)