Match the items of Column I and Column II on the basis of data given below:
![]()
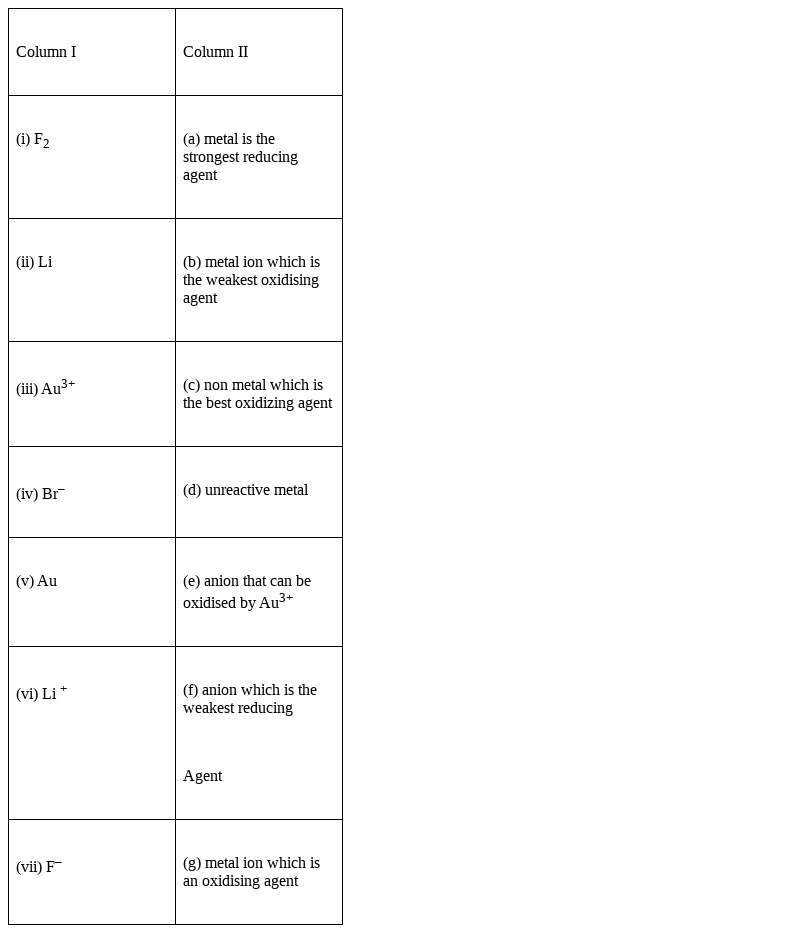
(i) F2 → (c) non-metal which is the best oxidizing agent
(ii) Li → (a) metal is the strongest reducing agent
(iii) Au3+ → (g) metal ion which is an oxidizing agent
(iv) Br– → (e) anion that can be oxidized by Au3+
(v) Au → (d) unreactive metal
(vi) Li +→ (b) metal ion which is the weakest oxidizing agent
(vii) F– → (f) anion which is the weakest reducing Agent
(i) We know, Fluoride is a non-metal and the standard electrode potential is +2.87V. High positive value means they are good oxidizing agent. Thus, F2 get easily reduced to F-.
(ii) Li+/Li have a standard electrode potential of -3.5V. Thus, this radox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 radox couple. In other words, they have the most negative potential value among the above chemical elements which makes Li metal a strongest reducing agent.
(iii) The standard electrode potential for Au3+/Au is + 1.4V. Thus, they are a weaker reducing agent than the H+/H2 radox couple. Positive standard electrode potential makes Au3+ a good oxidizing agent.
(iv) The standard electrode potential for this radox couple is +1.09V. Clearly, one can say that the standard electrode potential of this radox couple is less than that of Au3+/Au. Thus, Br- is weak oxidizing agent and stronger reducing agent than Au3+. Therefore, Br- anion can be oxidized by Au3+.
(v) Au3+ + 3e-→ Au(S)
Since, Au is in the solid state. Thus, its standard electrode potential will be zero. So, Au is an unreactive metal.
(vi) Li+/Li have a standard electrode potential of -3.5V. Thus, this radox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 radox couple. In other words, Li+ metal ion is the weakest oxidizing agent.
(vii) F2/F- have the standard electrode potential equal to +2.87V. High positive value of standard radox potential indicates that F2 is the best oxidizing agent, whereas, F- is the weakest reducing Agent.