Match the species given in Column I with the properties mentioned in Column II.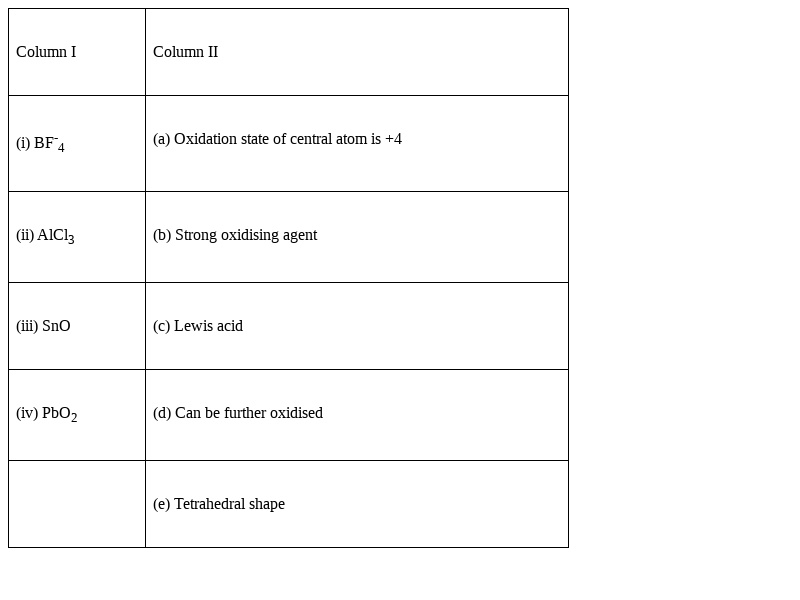
(i) BF-4- d) Can be further oxidised
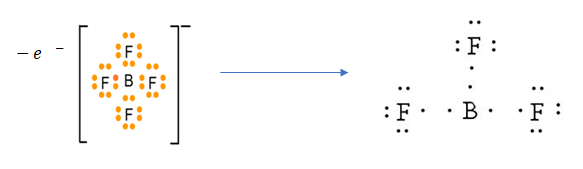
![]() Oxidation is a process which involves the gaining/ addition of Oxygen or removal of Hydrogen. It can also be stated as loss of electrons from any given ionic species or molecule. In the case of BF-4, it contains 4 Fluorine atoms, where 3 atoms covalently bind to Boron atom and the remaining Fluorine atom donates its lone pair of electron and forms BF-4. Now, the extra Fluorine atom if gets removed, it can be oxidised to form BF3 by losing extra electrons.
Oxidation is a process which involves the gaining/ addition of Oxygen or removal of Hydrogen. It can also be stated as loss of electrons from any given ionic species or molecule. In the case of BF-4, it contains 4 Fluorine atoms, where 3 atoms covalently bind to Boron atom and the remaining Fluorine atom donates its lone pair of electron and forms BF-4. Now, the extra Fluorine atom if gets removed, it can be oxidised to form BF3 by losing extra electrons.
ii) AlCl3– c) Lewis acid.
The species which are electron deficit or electrophilic in nature and are capable of accepting electrons are referred to as Lewis acids.In other words, any substance can act as Lewis acid which can accept lone pair or non-bonding electrons. In the case of AlCl3, Al has empty p- orbitals, thus, it can accept electrons in order to complete its octet. Therefore, it acts as a Lewis acid.
ii) AlCl3– e) Tetrahedral shape
At normal temperature, Aluminium Chloride exists in solid lattice structure. But as soon the temperature increases (180oC - 190oC), Aluminium chloride starts converting into liquid state by forming a more stable of dimer of AlCl3 and exhibits in tetrahedral structure.
![]()
![]()
iii) SnO – d) Can be further oxidised
Oxidation is a process which involves the gaining/ addition of Oxygen or removal of Hydrogen. It can also be stated as loss of electrons from any given ionic species or molecule. SnO can be further oxidised to form SnO2by addition of another Oxygen atom. Though, Stannous oxide is much more stable than Stannous dioxide.
iv) ![]() – b) stronger oxidising agent
– b) stronger oxidising agent
![]() is a stronger oxidising agent. Inert pair effect is defined as the inertness caused by ns electrons of outer shell during bonding because of poor shielding effect. Due to dominating effect of inert pair effect, +2 oxidation state is more stable, thereby making the conversion of
is a stronger oxidising agent. Inert pair effect is defined as the inertness caused by ns electrons of outer shell during bonding because of poor shielding effect. Due to dominating effect of inert pair effect, +2 oxidation state is more stable, thereby making the conversion of ![]() to
to ![]() easily making it a more stronger oxidising agent.
easily making it a more stronger oxidising agent.
iv) ![]() - (a) Oxidation state of central atom is +4
- (a) Oxidation state of central atom is +4
Lead has the oxidation number of +4 in Lead oxide.
Oxidation number is calculated as sum of oxidation number (ON) of all atoms in a polyatomic ion which is equated with the total charge of the molecule or ion.
Let ON of Pb be x
So, ON of each O = -2 and total charge = 0
So,
![]()
![]()
![]()