A long, straight wire carrying a current of 30 A is placed in an external, uniform magnetic field of 4.0 ×10–4 T parallel to the current. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at a point 2.0 cm away from the wire.
Given:
Current in the wire : I = 30 A
External Uniform magnetic field: BO = 4.0 ×10–4 T
Distance between the point and the wire : d = 2 cm = 0.02 m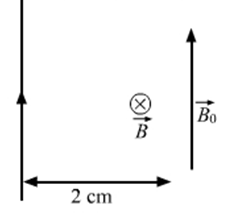
Here, B is the magnetic field due to wire. BO is parallel to the current in the wire. Using Right hand rule we can see that direction of magnetic field at the desired point is going into the plane (cross). This direction due to wire is perpendicular to the External magnetic field.![]() Formula used:
Formula used:
By Ampere’s Law for a current carrying wire is![]() Here, B is the magnitude of magnetic field, μ0 is the permeability of free space and μ0= 4π × 10-7 T mA-1 and d is the distance between the current carrying wire and the required point.
Here, B is the magnitude of magnetic field, μ0 is the permeability of free space and μ0= 4π × 10-7 T mA-1 and d is the distance between the current carrying wire and the required point.
Substituting we get,![]()
∴ B = 3× 10-4 T
As Magnetic field due to wire is perpendicular to the external magnetic field, the resultant net magnetic field would be:![]()
![]()
∴ Bnet = 5 × 10-4 T
Hence, the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at a point 2.0 cm away from the wire is 5 × 10-4 T.