Two long, straight wires, each carrying a current of 5A, are placed along the x-and y-axis respectively. The currents point along the positive directions of the axes.
Find the magnetic fields at the points (a) (1m, –1m), (b) (–1m, 1m) (c) (–1m, –1m) and (d) (1m, –1m).
Given:
Current in both the wires : I = 5 A.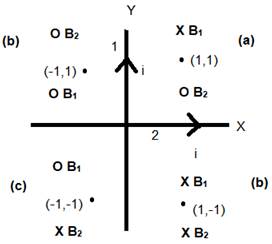
Wires 1 and 2 generate magnetic fields B1 and B2 respectively.
By right hand rule, direction of magnetic field in each quadrant due to wires 1 and is shown by X and O.
X : Field is going into the plane
O : Field is coming out of the plane.
Formula used:
By Ampere’s Law for a current carrying wire is![]() Where,
Where,
B is the magnitude of magnetic field,
μ0 is the permeability of free space and μ0= 4π × 10-7 T mA-1 d is the distance between the current carrying wire and the required point.
(a) At (1m,1m)
As we can see from the diagram at (1,1) the magnetic fields due to wire 1 and 2 are in opposite direction. (X and O)
Hence, net magnetic field would be zero.
(b) At (-1m , 1m)
Here, magnetic field due to wire 1 and 2 would add up as direction of magnetic field is same. ( O and O)
Thus B = BX + BY
BX is the magnetic field due to wire on x axis
BY is the magnetic field due to wire on y axis![]()
∴ B = 2× 10-6 T
This B would be along z-Axis.
(c) At (-1m,-1m)
As we can see from the diagram at (-1,-1) the magnetic fields due to wire 1 and 2 are in opposite direction. (O and X)
Hence, net magnetic field would be zero.
(d) At (1m,-1m)
Here, magnetic field due to wire 1 and 2 would add up as direction of magnetic field is same. ( X and X)
Thus B = BX + BY
BX is the magnetic field due to wire on x axis
BY is the magnetic field due to wire on y axis![]()
∴ B = 2× 10-6 T
This B would be along negative z-axis.